
Conducted Emission means that part of the electromagnetic (radio frequency) energy is transmitted through an external cable (cable) and a power line to form a conductive wave. This article describes conducted emissions via a power line. Differential mode and common mode noise "conducted EMI" can be divided into two categories: differential mode (DM) and common mode (CM). The differential mode is also called "symmetric mode" or "normal mode"; and the common mode is also called "asymmetric mode" or "ground leakage mode".
The noise generated by EMI is also divided into two categories: differential mode noise and common mode noise. In short, differential mode noise occurs when the current directions of the two power supply lines are opposite to each other, as shown in Figure 1(a). Common mode noise occurs when the current directions of all power supply lines are the same, as shown in Figure 1(b). In general, differential mode signals are usually what we want because they can carry useful data or signals. Common mode signals (noise) are unwanted side effects or 'by-products' of differential mode circuits. The biggest problem.
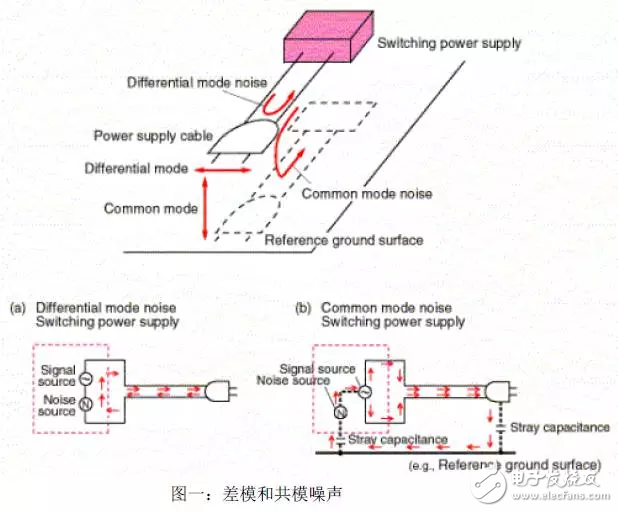
From Figure 1, it can be clearly seen that the occurrence of common mode noise is mostly caused by improper grounding of stray capacitors. This is why the common mode is also called the 'ground leakage mode'.
In Figure 2, the DM noise source is the push and pull current Idm through the L and N pairs. Because there is a DM noise source, no current flows through the ground line. The direction of the current of the noise varies according to the period of the alternating current.
The basic AC operating current provided by the power supply circuit is also differentially analog in nature. Because it flows into the L or N line and leaves through the L or N line. However, the differential mode current in Figure 2 does not contain this current. This is because the operating current is differential, but it is not noise. On the other hand, for a current source (signal source), if its fundamental frequency is twice the line frequency---100 or 120 Hz, it is still DC and is not noise. Even its harmonic frequency exceeds the limits of standard conductive EMI (150 kHz to 30 MHz). However, it must be noted that the operating current still retains the energy of the DC bias, which is provided for use with the filter choke, which can seriously affect the performance of the EMI filter. At this time, when an external current probe is used to measure the data, it is likely to cause measurement errors.
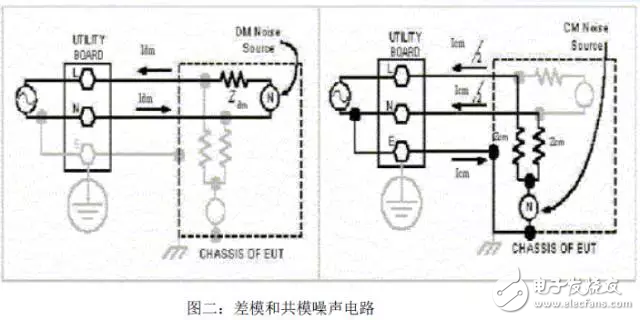
The CM noise source is grounded and the L and N lines have the same impedance Z. Therefore, it drives the same size circuit through the L and N lines. However, this assumes that the impedances of the two are equal in magnitude. It can be clearly observed that if the impedance of both sides is unbalanced, the 'asymmetric' common mode current will be distributed on the L and N lines. This seems to be a misnomer or does not match the original definition, because CM is also known as the 'asymmetric mode'. In order to avoid confusion, the mode at this time should be called 'nonsymmetric mode', so it is better to distinguish it from 'asymmetric mode'. In most power supply circuits, the EMI emitted in this mode is the most.
With unequal load or line impedance, the CM current can be effectively converted to a CM current and a DM current. For example, a DC-DC converter supplies power to a secondary system that has an unequal (unbalanced) impedance. Moreover, there is undetected common mode noise at the output of the DC-DC converter, which becomes a very real (differential) input voltage chop and is applied to the subsystem. There is no secondary system built-in "common mode rejecTIon raTIo (CMRR)" can be referenced, because this noise is not completely common mode. In the end, the system may have an error. Therefore, when generating the common mode current, it is necessary to reduce its size immediately. This is very important and is the primary task. Equalizing the impedance is a secondary task. In addition, due to the characteristics of the common mode and the differential mode, the frequency of the common mode current is greater than the frequency of the differential mode. Therefore, the common mode current produces a large amount of RF radiation. Moreover, inductive and capacitive coupling occurs with adjacent components and circuits. Typically, a 5uA common-mode current in a 1m long wire will produce more RF radiation than the Class B limit specified by the FCC. The FCC Class A specification limits the common mode current to a maximum of 15 uA. In addition, the shortest AC power cord is 1m according to the standard, so the length of the power cord cannot be shorter than 1m.
In a real power supply circuit, the differential mode noise source is much like a voltage source. The behavior of the common mode noise source is more like a current source, which makes the common mode noise more difficult to eliminate. It has the same flow path as all current sources. Because its path contains a chassis, the case can become a large, high-frequency antenna. Return path For noise current, what is the true return path? The distance between the physical paths of the entities is preferably as large as possible. Because no EMI filter is present, some of the noise current will be returned through various parasitic capacitances scattered throughout the area. The rest will be returned wirelessly, which is radiation; the resulting electromagnetic field affects adjacent conductors, producing very little current in these conductors. Finally, the sum of these very small return currents at the input of the power supply will remain at zero value and therefore will not violate [Kirchhoff's Law] - in a closed circuit, the algebraic sum of the current through a node is zero.
Laptop Stand 17 Inch Adjustable,Laptop Stand 17 Inch Alienware,Laptop Stand 17 Inch Bed,Laptop Stand 17 Inch Computer,etc.
Shenzhen Chengrong Technology Co.ltd is a high-quality enterprise specializing in metal stamping and CNC production for 12 years. The company mainly aims at the R&D, production and sales of Notebook Laptop Stands and Mobile Phone Stands. From the mold design and processing to machining and product surface oxidation, spraying treatment etc ,integration can fully meet the various processing needs of customers. Have a complete and scientific quality management system, strength and product quality are recognized and trusted by the industry, to meet changing economic and social needs .

Laptop Stand 17 Inch Adjustable,Laptop Stand 17 Inch Alienware,Laptop Stand 17 Inch Bed,Laptop Stand 17 Inch Computer
Shenzhen ChengRong Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.chengrongstand.com