Copper platoons are commonly used in distribution boxes to function as a means of delivering electrical current and connecting electrical equipment. Copper platoons have been widely used in electrical equipment, especially in power distribution units. The current carrying capacity of copper platoons has been asked many times by many friends, so today we can understand.


Copper and aluminum row flow rate fast query
Estimation method:
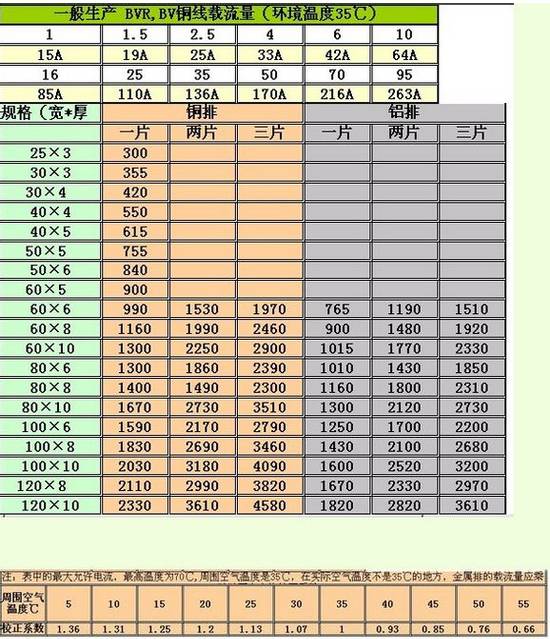
Single copper busbar current carrying capacity = width (mm) X thickness coefficient
Double busbar current carrying capacity = width (mm) X thickness coefficient X 1.5 (experience factor)
Copper and aluminum rows can also be squared, usually copper should be 5-8A/square.
Aluminum should be 3-5A/square
The current carrying capacity calculation method of commonly used copper bars:
Copper discharge current at 40 ° C = width * thickness coefficient
Row width (mm); thickness coefficient is:
When the busbar is 12 thick, it is 20; when it is 10 thick, it is 18;
The order is: [12-20,10-18,8-16,6-14,5-13,4-12].
Double layer copper row [40 ° C] = 1.56-1.58 single layer copper row [40 ° C] (according to the cross section size)
3-layer copper row [40 ° C] = 2 single-layer copper row [40 ° C]
4-layer copper row [40 ° C] = single-layer copper row [40 ° C] * 2.45 (this type of selection is not recommended, it is best to replace it with a special busbar)
Copper row [40 ° C] = copper row [25 ° C] * 0.85
Aluminum row [40 ° C] = copper row [40 ° C] / 1.3
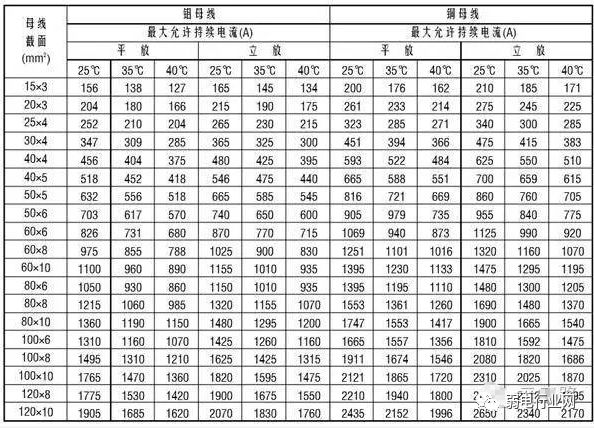
For example, the current flow rate of TMY100*10 is:
Single layer: 100*18=1800(A)[Check manual is 1860A];
Double layer: 2 (TMY100*10) current carrying capacity: 1860 * 1.58 = 2940 (A); [check manual is 2942A];
Three layers: 3 (TMY100*10) current carrying capacity: 1860 * 2 = 3720 (A) [check manual is 3780A]
All of the above calculations are accurate enough to be close to the manual data.
In addition, the copper discharge flow also has a very concise calculation formula:
Single rectangular copper row current = width * (row thickness + 8.5) A
For example: 15*3 at 40°C, the current carrying capacity = 15*11.5=172.5A
100*8 40°C current carrying capacity=100*16.5=1650A
Double-layer current carrying capacity = 1.5 times single-layer current carrying capacity
Three-layer current carrying capacity = 2.0 times single-layer current carrying capacity
Mouth
The aluminum discharge current should be fast, and the width factor is multiplied;
Thick three rows wide by ten, the last four rows wide by twelve.
Add one to add up one by one, and the copper row is multiplied by one.
The current carrying capacity of the busbar is related to its cross-sectional size.
Therefore, the current carrying capacity can be directly calculated by the thickness and width dimensions of the bus bar.
According to the mouth, for a certain thickness of aluminum row, its current carrying capacity can be multiplied by a factor.
The aluminum row with a thickness of 3 mm has a carrying capacity of width × 10 and a thickness of 4 mm. The aluminum row flow rate is width × 12.
"Add one in turn to add up" is to say that the thickness is increased by one millimeter, and the coefficient of the width is multiplied by one, and the aluminum row with a thick millimeter thickness starts, and the following table is arranged in order:
Thickness (mm) 3 4 5 6 8 10
Current carrying capacity (A) width × 10 width × 12 width × 13 width × 14 width × 16 width × 18
Note: The aluminum row thickness is not available in 7mm and 9mm sizes.
Example: What is the flow rate of 40×4 mother aluminum?
Solution: According to the mouth, the thickness of the 4 load is ×12, so 40×12=480A
Example: What is the current carrying capacity of a 60×6 aluminum busbar?
Solution: 60×14=840A
"The copper platoon is multiplied by a little three" said that the current carrying capacity of the copper platoon is 30% larger than that of the aluminum platoon of the same specification.
Therefore, when seeking the copper discharge flow rate, first consider it as an aluminum row. After calculating according to the above method, multiply by 1.3.
Example: seeking 50 × 13 × 1.3 = 845 amps
The current carrying capacity of the busbar is also related to factors such as ambient temperature, multiple busbars, horizontal busbars, and vertical placement.
When the general ambient temperature is often higher than 250C or the DC bus is juxtaposed, it can be treated at 10%.
When the 2, 3, and 4 busbars are used in parallel, they can be used for 8, 7 or 6 fold respectively.
Fiber Optic Distribution Box,Fiber Optic Breakout Box,Fibre Optic Breakout Box,Fibre Break Out Box
Cixi Dani Plastic Products Co.,Ltd , https://www.dani-fiber-optic.com