[Abstract] A brief introduction to the recently developed personal area network, detailed discussion of the characteristics of Bluetooth technology, functional units and protocol systems, and finally its prospects for development.
Keywords: personal area network Bluetooth technology functional unit protocol system
1 Introduction of Personal Local Area Network (PAN) With the development of network communication technology, a new small wireless local area network is quietly emerging. This is a special small local area network called Personal Area Network (Personal Area Network) in the industry. The basic idea of ​​PAN is: to realize the intelligent interconnection of personal information terminals in a wireless manner, and to establish a personalized information network for home or office.
PAN is mainly used in homes and small office work occasions. It can realize functions such as voice communication, data communication, interconnection of information appliances and office appliances, automatic exchange of information, Internet access services, etc. It is the construction of the future information-based home and office environment Emerging Technologies. With the rapid development of network technology and the development of information appliances, its development prospects are broad.
PAN is mainly suitable for indoor short-distance communication. Correspondingly, PAN has some of its own characteristics, such as small device size, easy to carry, small transceiver power, high working frequency band, relatively stable communication environment, and low cost. QoS etc.
There are many PAN implementation technologies, including Bluetooth, IrDA, Home RF, and UWB (Ultra-Wideband Radio). Among them, Bluetooth technology, as one of the mainstream technologies, is supported by manufacturers like Ericsson, Nokia, Intel, IBM and others. Its development momentum is strong, and it has become a gorgeous flower in the PAN technology park. In view of this, the following will give a preliminary introduction.
2 Bluetooth technology development overview and characteristics Bluetooth (Bluetooth) technology is a new technology to achieve short-distance wireless transmission of voice and data, supports point-to-point, point-to-multipoint communication. The technology was proposed and promoted by companies such as Ericsson, Nokia, Intel, IBM and Toshiba. Since 1998, the Bluetooth 1.0A and Bluetooth 1.0B standards have been successively launched, and the Bluetooth 2.0 standard will also be launched soon. This greatly promoted the development of PAN technology. IEEE specially established IEEE 802.15 group to study PAN technology based on Bluetooth technology. Bluetooth technology has the following characteristics:
(1) The device is wirelessly connected to form a small PAN, and can provide the function of accessing the data network, and can be interconnected with Internet.
(2) Working in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, no need to apply for a frequency license.
(3) Adopt 1600hop / s fast frequency hopping technology, which provides a certain degree of physical layer security guarantee.
(4) The use of forward error correction coding (FEC) technology reduces the bit error rate and guarantees the communication quality.
(5) Using FM modulation, the equipment is simple.
(6) Support point-to-multipoint communication, with the function of automatically querying equipment and service types.
(7) The protocol system is complete, fully supports the existing high-level agreements, and has multiple working modes.
(8) Support multi-channel transmission, can realize asymmetric connection.
(9) Support two switching forms: circuit switching and packet switching.
(10) The equipment is small in size, easy to carry or move, and low in cost.
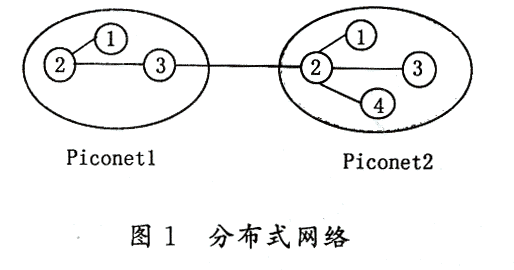
3 The composition of Bluetooth system and its topology The devices that support Bluetooth technology form a network in a specific way, which we call piconet (Piconet). Piconet consists of up to eight devices, all Bluetooth devices are peer-to-peer and work in the same way. However, when the piconet is established, only one device's clock and frequency hopping sequence are used to synchronize other devices. This device is called the master unit (Master unit), and the other synchronized devices are called slave units (Slave unit). The devices in the piconet have a unique MAC address (MACadress), which is used to distinguish and identify each other. The address is represented by 3 bits. The devices in the piconet can be in the Sleep state (Parketstate), Listening (Sniffstate) state, or Hold (Hodestate) state. When in the sleep state, the device has no MAC address. A distributed network (Scatter Network) is formed by several independent asynchronous piconets, so PAN can be considered as a distributed network. Figure 1 shows the network topology.
4 Bluetooth function unit
4.1 The Bluetooth system of the radio frequency unit uses an omnidirectional antenna to support point-to-multipoint communication, so that multiple Bluetooth devices can share LAN resources; support terminal mobility, easier to query and discover devices. Signal transmission is not affected by line-of-sight and is easy to network. The transmit power of the antenna is designed at 0 dBm, which meets the FCC requirements for the ISM band. The transmission power can reach 100mW, the system is between 2.402GHz and 2.480GHz, and 79 frequency points of 1MHz are used for frequency hopping. The designed communication distance is 10 cm to 10 meters, and the increased transmission power can reach 100 meters.
4.2 Baseband control unit The Bluetooth baseband control unit implements the baseband protocol and other low-level connection protocols, and specifically performs three functions: network establishment, error control, verification, and encryption.
(1) Network establishment Before the piconet is established, all Bluetooth devices are in a waiting state. In this state, the device monitors the information every 1.28s. Once the device is woken up, it will monitor the information on the preset 32 ​​frequency hopping frequencies. The connection process is initiated by the master device. If the MAC of a device is known, the connection is established using paging information; if the MAC is unknown, the connection is established using paging query information. In the initial paging state, the master device sends the same string of paging information to the slave device on 16 frequency hopping frequencies. If no response is received, the master device sends paging information on the other 16 frequency hopping frequencies. When the required slave device answers, the connection is established and the network is established. Bluetooth baseband technology supports two connection methods:
· Connection-oriented (SCO) synchronous transmission method: mainly used for voice transmission.
· Asynchronous transmission for connectionless (ACL): mainly used for the transmission of packet data.
It should be noted that in the same piconet, different master and slave devices can use different connection methods, and the connection method can be changed in one communication. Each connection mode supports 16 different packet types, including four control packets, which are common to SCO and ACL. Both connection methods use time division duplex (TDD) communication. SCO is a symmetric connection and supports real-time voice transmission. The master and slave devices can send data without polling. SCO packets can be either voice or data. When an interruption occurs, only the data portion needs to be retransmitted. ACL is a packet-oriented connection, supports both symmetric and asymmetric transmission traffic, and also supports broadcast information. In the ACL mode, the master device controls the link bandwidth and is responsible for the bandwidth allocation of the slave device, and the slave device sends data according to polling.
(2) The error control baseband controller uses three error correction methods: 1/3 forward error correction coding (FEC), 2/3 forward error correction coding, and automatic request retransmission (ARQ). The purpose of using FEC coding is to reduce the number of data retransmissions, but in an error-free environment, the FEC check bit is useless and reduces the data throughput, so whether to add FEC check for service data should depend on the specific situation. For packet headers containing important connection information and error correction information, always use 1/3 FEC check code for protection transmission. For data transmission that needs to be confirmed in the next time slot after transmission, the ARQ method is used. Sending ACK back means that both the header information check and the CRC check are correct; otherwise, NACK is sent back.
(3) Verification and encryption The physical layer provides verification and encryption services. Verification and encryption use a password / response method. During the connection process, one verification or two verifications may be required, or no verification. Authentication is an important part of the Bluetooth system, which allows users to add trusted Bluetooth devices. The Bluetooth system uses stream cipher encryption technology, which is convenient for hardware implementation. The key length can be 0, 40, 64, 128 bits. The Bluetooth device must check the key every time the link is established. This key is used for authentication during communication. And encryption. The key is managed by high-level software. The purpose of Bluetooth authentication and encryption is to provide an appropriate level of protection. If users have a higher level of confidentiality requirements, they need to use transport layer and application layer security mechanisms.
4.3 Link management unit The link management unit implements the establishment, verification, link configuration, and other protocols of communication links. The link manager can discover other link managers and establish communication links through the link management protocol (LMP). The link manager uses the services provided by the link controller (LC) to achieve the above functions. The functions implemented by LC are: receiving and sending data, device number request, link address query, connection establishment, verification, negotiation of connection establishment method, determining the frame type of the packet, setting the working mode of the device (listening, sleeping or keeping).
4.4 Software functional unit The purpose of the Bluetooth plan is to ensure that any Bluetooth device can communicate with each other. Therefore, Bluetooth devices must be able to recognize each other, and identify the high-level functions supported by each other by installing appropriate software. Interoperability requires the same application layer protocol. Software interoperability refers to the multiplexing of link-level protocols, the discovery of devices and services, and the segmentation and reassembly of packets. These functions are performed by Bluetooth mobile phones, handheld devices, and laptop computers. The Bluetooth software structural unit utilizes existing specifications, such as OBEX, vCard / vCalendar, HID, WAP, PPP, and TCP / IP protocol specifications, rather than developing new protocols. The main functions of the software unit are: discovery of Bluetooth devices, communication with peripheral devices, audio communication and call control, exchange of business cards and phone numbers, etc.
5 Bluetooth technology protocol system Bluetooth protocol stack shown in Figure 2. The complete Bluetooth protocol includes Bluetooth specific protocols (such as LMP and L2CAP) and non-specific protocols (such as object exchange protocol OBEX and transmission control protocol TCP). The design principle of the protocol and protocol stack is to make full use of existing high-level protocols to ensure the integration of the existing protocol with Bluetooth technology and interoperability between various applications, and make full use of software and hardware systems compatible with Bluetooth technology specifications.

The Bluetooth protocol system can be divided into two categories: core protocols and application protocols. The core protocols include baseband protocol (Baseband) link management protocol (LMP), logical link control and adaptation protocol (L2CAP) and service discovery protocol (SDP).
5.1 Core protocol (1) Baseband protocol (Baseband)
The baseband protocol discovers Bluetooth devices at the beginning of the establishment of the network, and together with the link control layer ensures that wireless connections are established between the device units in the piconet. Voice-coded data is transmitted directly through the baseband protocol. Call control commands (TCS BIN and AT Commands) are based on the virtual serial port protocol RFCOMM, which is processed through L2CP and enters baseband transmission.
(2) Link Management Protocol (LMP)
The link management protocol is responsible for the establishment and control of wireless connections between Bluetooth devices. Through the initiation, exchange and verification of the connection, identity verification and encryption are carried out, and the size of the baseband data packet is determined through negotiation; the power mode and duty cycle of the wireless device are controlled, and the connection status of the device unit in the piconet.
(3) Logical link control and adaptation protocol (L2CAP)
When business data does not pass through LMP, L2CAP provides services for the upper layer. L2CAP uses multiplexing technology, segmentation and reassembly technology, group extraction technology, allowing high-level protocols to send and receive data packets with 64K bytes. However, L2CAP only supports ACL connections.
(4) Service Discovery Protocol (SDP)
Service discovery is the basis of all user modes. Using SDP can provide device information and service types to establish connections between Bluetooth devices.
5.2 Application protocol Bluetooth applications include three types: OBEX-based object switching, PPP-based Internet applications, and voice communication applications. The corresponding application protocols are:
· Cable replacement protocol Simulate RS-232 control data signal on the Bluetooth baseband protocol to provide services for the upper layer protocol that uses serial lines to transmit data.
· Binary telephone control protocol and AT command set telephone control protocol defines the control commands for establishing voice and data calls between Bluetooth devices and the command set for controlling mobile phones and modems in multi-user mode.
OBEX-based object exchange protocol is similar to the HTTP protocol, using a client-server model and an interface independent of the transmission mechanism and transmission application program to complete electronic business card exchange (vCard), electronic calendar and its exchange (vCal), electronic notebook vNot e), electronic message (vMessage), etc.
The optional application protocol TCP / UDP / IP is used to complete the communication between the Bluetooth device and the Internet. WAP transfers Internet information and telephone-transmitted services to digital cellular phones or other wireless terminals. Based on L2CAP, using different protocol stack groups to form corresponding protocol stacks can realize different user modes, such as file transfer mode, synchronization mode, LAN access mode, one-machine three-use phone mode, Internet bridge mode, etc.
6 Conclusion Looking back at the development of network technology, it can be seen that the development of local area networks is the foundation and backbone of network development. As far as network coverage is concerned, the wide area network connects countless computer terminals into an information network containing extremely rich information resources, making the entire earth gradually become a veritable global village, which has greatly changed people's lifestyles. Traditional WAN networking and transmission technologies are relatively mature, and its research focus is turning to all-optical network research to improve the transmission rate and eliminate bandwidth bottlenecks. At the same time, the local area network is also developing in the direction of miniaturization, which is the so-called personal local area network. The development of personal local area network uses wireless technology to interconnect personal home equipment or office equipment to form a small local area network, realize the networking of the equipment and access the Internet as a whole, so that the network truly penetrates into the home or office and further expands the network Coverage.
Bluetooth technology is the mainstream technology of personal local area networks. Although its data transmission rate is relatively low, and there are other technical problems in applications such as hardware compatibility and identification of the same device that need to be resolved, its advantages are very prominent, and many manufacturers The production equipment supports Bluetooth technology, so the development prospect of Bluetooth technology is very broad, I believe it will occupy the dominant position in the future personal network market. Therefore, we must pay full attention to this emerging technology, strengthen research and development work, and promote the development of personal network technology.
1 Bluetooth SIG. SpecificaTIon of the Bluetooth SystemCore, version 1.0B. http: // luetooth. com, December 1st 1999
2 Bluetooth SIG. SpecificaTIon of the Bluetooth SystemProfiles, version 1.0B. h ttp: //. com, December 1st 1999
3 Riku Mettala. Bluetooth Protocol Architecture. http: //. com, July 15th 1999
4 Riku Mettala. Bluetooth Security Architecture. http: //. com, July 15th 1999
5 Riku Mettala. Bluetooth PC Card Transport Layer. http: //. com, July 15th 1999
6 Guo Feng, Zeng Xingwen, etc. Wireless LAN. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 1997
Keywords: personal area network Bluetooth technology functional unit protocol system
1 Introduction of Personal Local Area Network (PAN) With the development of network communication technology, a new small wireless local area network is quietly emerging. This is a special small local area network called Personal Area Network (Personal Area Network) in the industry. The basic idea of ​​PAN is: to realize the intelligent interconnection of personal information terminals in a wireless manner, and to establish a personalized information network for home or office.
PAN is mainly used in homes and small office work occasions. It can realize functions such as voice communication, data communication, interconnection of information appliances and office appliances, automatic exchange of information, Internet access services, etc. It is the construction of the future information-based home and office environment Emerging Technologies. With the rapid development of network technology and the development of information appliances, its development prospects are broad.
PAN is mainly suitable for indoor short-distance communication. Correspondingly, PAN has some of its own characteristics, such as small device size, easy to carry, small transceiver power, high working frequency band, relatively stable communication environment, and low cost. QoS etc.
There are many PAN implementation technologies, including Bluetooth, IrDA, Home RF, and UWB (Ultra-Wideband Radio). Among them, Bluetooth technology, as one of the mainstream technologies, is supported by manufacturers like Ericsson, Nokia, Intel, IBM and others. Its development momentum is strong, and it has become a gorgeous flower in the PAN technology park. In view of this, the following will give a preliminary introduction.
2 Bluetooth technology development overview and characteristics Bluetooth (Bluetooth) technology is a new technology to achieve short-distance wireless transmission of voice and data, supports point-to-point, point-to-multipoint communication. The technology was proposed and promoted by companies such as Ericsson, Nokia, Intel, IBM and Toshiba. Since 1998, the Bluetooth 1.0A and Bluetooth 1.0B standards have been successively launched, and the Bluetooth 2.0 standard will also be launched soon. This greatly promoted the development of PAN technology. IEEE specially established IEEE 802.15 group to study PAN technology based on Bluetooth technology. Bluetooth technology has the following characteristics:
(1) The device is wirelessly connected to form a small PAN, and can provide the function of accessing the data network, and can be interconnected with Internet.
(2) Working in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, no need to apply for a frequency license.
(3) Adopt 1600hop / s fast frequency hopping technology, which provides a certain degree of physical layer security guarantee.
(4) The use of forward error correction coding (FEC) technology reduces the bit error rate and guarantees the communication quality.
(5) Using FM modulation, the equipment is simple.
(6) Support point-to-multipoint communication, with the function of automatically querying equipment and service types.
(7) The protocol system is complete, fully supports the existing high-level agreements, and has multiple working modes.
(8) Support multi-channel transmission, can realize asymmetric connection.
(9) Support two switching forms: circuit switching and packet switching.
(10) The equipment is small in size, easy to carry or move, and low in cost.
3 The composition of Bluetooth system and its topology The devices that support Bluetooth technology form a network in a specific way, which we call piconet (Piconet). Piconet consists of up to eight devices, all Bluetooth devices are peer-to-peer and work in the same way. However, when the piconet is established, only one device's clock and frequency hopping sequence are used to synchronize other devices. This device is called the master unit (Master unit), and the other synchronized devices are called slave units (Slave unit). The devices in the piconet have a unique MAC address (MACadress), which is used to distinguish and identify each other. The address is represented by 3 bits. The devices in the piconet can be in the Sleep state (Parketstate), Listening (Sniffstate) state, or Hold (Hodestate) state. When in the sleep state, the device has no MAC address. A distributed network (Scatter Network) is formed by several independent asynchronous piconets, so PAN can be considered as a distributed network. Figure 1 shows the network topology.

4 Bluetooth function unit
4.1 The Bluetooth system of the radio frequency unit uses an omnidirectional antenna to support point-to-multipoint communication, so that multiple Bluetooth devices can share LAN resources; support terminal mobility, easier to query and discover devices. Signal transmission is not affected by line-of-sight and is easy to network. The transmit power of the antenna is designed at 0 dBm, which meets the FCC requirements for the ISM band. The transmission power can reach 100mW, the system is between 2.402GHz and 2.480GHz, and 79 frequency points of 1MHz are used for frequency hopping. The designed communication distance is 10 cm to 10 meters, and the increased transmission power can reach 100 meters.
4.2 Baseband control unit The Bluetooth baseband control unit implements the baseband protocol and other low-level connection protocols, and specifically performs three functions: network establishment, error control, verification, and encryption.
(1) Network establishment Before the piconet is established, all Bluetooth devices are in a waiting state. In this state, the device monitors the information every 1.28s. Once the device is woken up, it will monitor the information on the preset 32 ​​frequency hopping frequencies. The connection process is initiated by the master device. If the MAC of a device is known, the connection is established using paging information; if the MAC is unknown, the connection is established using paging query information. In the initial paging state, the master device sends the same string of paging information to the slave device on 16 frequency hopping frequencies. If no response is received, the master device sends paging information on the other 16 frequency hopping frequencies. When the required slave device answers, the connection is established and the network is established. Bluetooth baseband technology supports two connection methods:
· Connection-oriented (SCO) synchronous transmission method: mainly used for voice transmission.
· Asynchronous transmission for connectionless (ACL): mainly used for the transmission of packet data.
It should be noted that in the same piconet, different master and slave devices can use different connection methods, and the connection method can be changed in one communication. Each connection mode supports 16 different packet types, including four control packets, which are common to SCO and ACL. Both connection methods use time division duplex (TDD) communication. SCO is a symmetric connection and supports real-time voice transmission. The master and slave devices can send data without polling. SCO packets can be either voice or data. When an interruption occurs, only the data portion needs to be retransmitted. ACL is a packet-oriented connection, supports both symmetric and asymmetric transmission traffic, and also supports broadcast information. In the ACL mode, the master device controls the link bandwidth and is responsible for the bandwidth allocation of the slave device, and the slave device sends data according to polling.
(2) The error control baseband controller uses three error correction methods: 1/3 forward error correction coding (FEC), 2/3 forward error correction coding, and automatic request retransmission (ARQ). The purpose of using FEC coding is to reduce the number of data retransmissions, but in an error-free environment, the FEC check bit is useless and reduces the data throughput, so whether to add FEC check for service data should depend on the specific situation. For packet headers containing important connection information and error correction information, always use 1/3 FEC check code for protection transmission. For data transmission that needs to be confirmed in the next time slot after transmission, the ARQ method is used. Sending ACK back means that both the header information check and the CRC check are correct; otherwise, NACK is sent back.
(3) Verification and encryption The physical layer provides verification and encryption services. Verification and encryption use a password / response method. During the connection process, one verification or two verifications may be required, or no verification. Authentication is an important part of the Bluetooth system, which allows users to add trusted Bluetooth devices. The Bluetooth system uses stream cipher encryption technology, which is convenient for hardware implementation. The key length can be 0, 40, 64, 128 bits. The Bluetooth device must check the key every time the link is established. This key is used for authentication during communication. And encryption. The key is managed by high-level software. The purpose of Bluetooth authentication and encryption is to provide an appropriate level of protection. If users have a higher level of confidentiality requirements, they need to use transport layer and application layer security mechanisms.
4.3 Link management unit The link management unit implements the establishment, verification, link configuration, and other protocols of communication links. The link manager can discover other link managers and establish communication links through the link management protocol (LMP). The link manager uses the services provided by the link controller (LC) to achieve the above functions. The functions implemented by LC are: receiving and sending data, device number request, link address query, connection establishment, verification, negotiation of connection establishment method, determining the frame type of the packet, setting the working mode of the device (listening, sleeping or keeping).
4.4 Software functional unit The purpose of the Bluetooth plan is to ensure that any Bluetooth device can communicate with each other. Therefore, Bluetooth devices must be able to recognize each other, and identify the high-level functions supported by each other by installing appropriate software. Interoperability requires the same application layer protocol. Software interoperability refers to the multiplexing of link-level protocols, the discovery of devices and services, and the segmentation and reassembly of packets. These functions are performed by Bluetooth mobile phones, handheld devices, and laptop computers. The Bluetooth software structural unit utilizes existing specifications, such as OBEX, vCard / vCalendar, HID, WAP, PPP, and TCP / IP protocol specifications, rather than developing new protocols. The main functions of the software unit are: discovery of Bluetooth devices, communication with peripheral devices, audio communication and call control, exchange of business cards and phone numbers, etc.
5 Bluetooth technology protocol system Bluetooth protocol stack shown in Figure 2. The complete Bluetooth protocol includes Bluetooth specific protocols (such as LMP and L2CAP) and non-specific protocols (such as object exchange protocol OBEX and transmission control protocol TCP). The design principle of the protocol and protocol stack is to make full use of existing high-level protocols to ensure the integration of the existing protocol with Bluetooth technology and interoperability between various applications, and make full use of software and hardware systems compatible with Bluetooth technology specifications.

The Bluetooth protocol system can be divided into two categories: core protocols and application protocols. The core protocols include baseband protocol (Baseband) link management protocol (LMP), logical link control and adaptation protocol (L2CAP) and service discovery protocol (SDP).
5.1 Core protocol (1) Baseband protocol (Baseband)
The baseband protocol discovers Bluetooth devices at the beginning of the establishment of the network, and together with the link control layer ensures that wireless connections are established between the device units in the piconet. Voice-coded data is transmitted directly through the baseband protocol. Call control commands (TCS BIN and AT Commands) are based on the virtual serial port protocol RFCOMM, which is processed through L2CP and enters baseband transmission.
(2) Link Management Protocol (LMP)
The link management protocol is responsible for the establishment and control of wireless connections between Bluetooth devices. Through the initiation, exchange and verification of the connection, identity verification and encryption are carried out, and the size of the baseband data packet is determined through negotiation; the power mode and duty cycle of the wireless device are controlled, and the connection status of the device unit in the piconet.
(3) Logical link control and adaptation protocol (L2CAP)
When business data does not pass through LMP, L2CAP provides services for the upper layer. L2CAP uses multiplexing technology, segmentation and reassembly technology, group extraction technology, allowing high-level protocols to send and receive data packets with 64K bytes. However, L2CAP only supports ACL connections.
(4) Service Discovery Protocol (SDP)
Service discovery is the basis of all user modes. Using SDP can provide device information and service types to establish connections between Bluetooth devices.
5.2 Application protocol Bluetooth applications include three types: OBEX-based object switching, PPP-based Internet applications, and voice communication applications. The corresponding application protocols are:
· Cable replacement protocol Simulate RS-232 control data signal on the Bluetooth baseband protocol to provide services for the upper layer protocol that uses serial lines to transmit data.
· Binary telephone control protocol and AT command set telephone control protocol defines the control commands for establishing voice and data calls between Bluetooth devices and the command set for controlling mobile phones and modems in multi-user mode.
OBEX-based object exchange protocol is similar to the HTTP protocol, using a client-server model and an interface independent of the transmission mechanism and transmission application program to complete electronic business card exchange (vCard), electronic calendar and its exchange (vCal), electronic notebook vNot e), electronic message (vMessage), etc.
The optional application protocol TCP / UDP / IP is used to complete the communication between the Bluetooth device and the Internet. WAP transfers Internet information and telephone-transmitted services to digital cellular phones or other wireless terminals. Based on L2CAP, using different protocol stack groups to form corresponding protocol stacks can realize different user modes, such as file transfer mode, synchronization mode, LAN access mode, one-machine three-use phone mode, Internet bridge mode, etc.
6 Conclusion Looking back at the development of network technology, it can be seen that the development of local area networks is the foundation and backbone of network development. As far as network coverage is concerned, the wide area network connects countless computer terminals into an information network containing extremely rich information resources, making the entire earth gradually become a veritable global village, which has greatly changed people's lifestyles. Traditional WAN networking and transmission technologies are relatively mature, and its research focus is turning to all-optical network research to improve the transmission rate and eliminate bandwidth bottlenecks. At the same time, the local area network is also developing in the direction of miniaturization, which is the so-called personal local area network. The development of personal local area network uses wireless technology to interconnect personal home equipment or office equipment to form a small local area network, realize the networking of the equipment and access the Internet as a whole, so that the network truly penetrates into the home or office and further expands the network Coverage.
Bluetooth technology is the mainstream technology of personal local area networks. Although its data transmission rate is relatively low, and there are other technical problems in applications such as hardware compatibility and identification of the same device that need to be resolved, its advantages are very prominent, and many manufacturers The production equipment supports Bluetooth technology, so the development prospect of Bluetooth technology is very broad, I believe it will occupy the dominant position in the future personal network market. Therefore, we must pay full attention to this emerging technology, strengthen research and development work, and promote the development of personal network technology.
references
2 Bluetooth SIG. SpecificaTIon of the Bluetooth SystemProfiles, version 1.0B. h ttp: //. com, December 1st 1999
3 Riku Mettala. Bluetooth Protocol Architecture. http: //. com, July 15th 1999
4 Riku Mettala. Bluetooth Security Architecture. http: //. com, July 15th 1999
5 Riku Mettala. Bluetooth PC Card Transport Layer. http: //. com, July 15th 1999
6 Guo Feng, Zeng Xingwen, etc. Wireless LAN. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 1997
Fiber Optic Ip68 Enclosure,Ftta Ip68 Hardened Connections Device,Ftta Ip68 Hardened Connections Fast,Fiber Optic Ip68 Enclosure Adapter
Huizhou Fibercan Industrial Co.Ltd , https://www.fibercannetworks.com