In order to improve the accuracy of the tire pressure monitoring system, a mathematical model of multi-sensor information fusion was established by Bayesian method. The model combines the complementary information of temperature and pressure of the tire, which has the advantages of information integrity, uniformity, diversity and fault tolerance compared with the traditional tire pressure monitoring system. Experiments show that the system can achieve the role of comprehensive early warning of puncture, and provides an effective method for monitoring tire pressure and temperature. It is reliable and suitable for promotion.
This article refers to the address: http://
introduction
Multi-sensor information fusion is an emerging multi-disciplinary research field, involving signal processing, probability statistics, information theory, pattern recognition, artificial intelligence, fuzzy mathematics and other theories. It is the result of human beings' ability to imitate their own information processing. In a nutshell, multi-sensor information fusion technology refers to the “merging†of information from multiple sources through certain algorithms to produce more reliable and accurate information than the data obtained by a single sensor, and to make the most reliable based on this information. Decision making. In order to improve the accuracy of Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS), improve the accuracy of alarms, and reduce false positives and false negatives, this paper discusses the application of multi-sensor information fusion technology in TPMS.
Research Background
The emergence of the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) was triggered by the quality of the tires of Bridgestone/Folster (BSF). This quality problem caused a large number of punctures and rollover accidents. The main cause of the accident was insufficient tire pressure and excessive heat generation, which destroyed its internal structure and caused a puncture. On November 1, 2000, US President Bill Clinton signed a proposal to amend Congress to amend the Federal Transportation Act, requiring all new light vehicles to be standard as standard after 2003. In July 2001, in response to US Congress requirements for the installation of TPMS legislation for vehicles, the US Department of Transportation and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration jointly conducted two existing TPMS systems. For evaluation, the report used TPMS as a special vocabulary for the first time.
According to the tire pressure monitoring method, it is mainly divided into two categories: indirect and direct. Indirect (Warn-Speed ​​Based TPMS: WSB TPMS) is a wheel speed sensor of the automotive ABS system to compare the difference in speed between tires to monitor tire pressure. The Pressure - SensorBased TPMS (PSB TPMS) uses a pressure sensor installed in each tire to directly measure and monitor the tire pressure. When the tire pressure is not within the given range, the system will Automatic alarm. It is predicted that by the time the National Highway Safety Administration (N HTSA) of the United States revises the TPMS regulations in 2005, it may be possible to replace the transitional indirect with direct. At present, the TPMS installed in foreign top-class cars are direct, and there is great room for direct research and development.
Literature (Li Wenyin, Zhou Bin. Design and implementation of tire pressure monitoring system; Jeff B. Tire pressure monitoring: an industry under pressure) detailed introduction to a design idea of ​​direct TPMS, the hardware is Motorola's sensor MPXY8020A, receiver MC33594, MCU and transmitter integrated chip MC68HC908RF2. The MPXY8020A has four modes of operation: standby, measuring pressure, measuring temperature, reading data; MC68HC908RF2 can transmit data at 315MHz or 434MHz depending on all crystal oscillators; MC33594 can receive and demodulate OO K or FSK modulated Manchester encoded data, using FSK Modulation, with a matched antenna, has a sensitivity of -105dBm. In terms of software design, the method of obtaining data adopts the threshold check method. The communication protocol adopts Manchester coding, FSK signal modulation mode and transmission rate of 9600 BPS, which is a mature product at present.
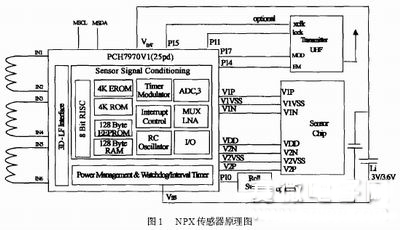
NPX sensor
Due to the limitations of the working environment, the selected sensor must be ultra-small and save power. GENova Sensor's NPX series sensors are a new generation of tire pressure monitoring system sensors based on the NPP series. They are 16mm × 8mm × 3mm (including lead) and are equipped with temperature, pressure and voltage sensors and ASICs. (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) The controller is composed of a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) core module with a large number of peripheral devices. The microcontroller (μC) program can be directly loaded into the EPROM through the programmer during development. The sensor can choose from three main measurement methods: pressure (P), temperature (T) and battery voltage (U). The microcontroller in the sensor is responsible for the measurement of the signal and converts the temperature into a pressure signal, which is then sent to the receiver's microcontroller for re-fusion. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 1.
Among them, the temperature sensor is designed in the ASIC circuit and has a characteristic proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT). The Transmit ter U HF shown in the figure is an externally connected transmitter, not the sensor itself.
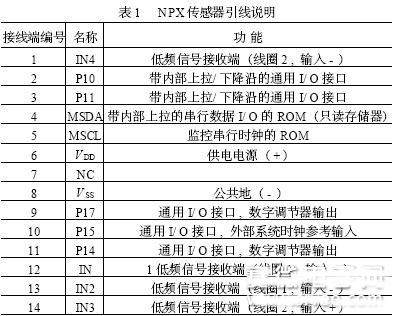
The sensor has 14 leads, and the name and function of each lead are shown in Table 1.
It measures a pressure range of 100 to 450 kPa, a temperature range of -40 to 125 °C, and an operating ambient temperature range of -40 to 175 °C. It can operate for 30 minutes when the ambient temperature is between 150 and 175 °C. The pressure signal is 12 bits obtained by the dual temperature calibration method, and the temperature signal is 10 bits, so the pressure and temperature signals are distinguishable. The NPX sensor is currently the most complete sensor system, but it does not have an integrated transmitter. If domestic manufacturers make breakthroughs in this area, there will be a broad market and can contribute to the development of China's TPMS, revitalizing China's tires. industry.
Tire pressure monitoring system
Choice of fusion method
For tires, pressure is their life, and temperature is not negligible. At present, the main quality problems of tires such as "shoulder space" and "bead delamination" are caused by excessive temperature in these parts. The author is developing “Automobile tire safety performance intelligenceâ€, so it is necessary to combine temperature and pressure signals in its model.
This paper uses the Bayes method to combine pressure and pressure from temperature conversion. This method does not require any historical statistics and expert knowledge about tire pressure and temperature. For the measurement results of only a limited number of pressure and temperature sensors (integrated sensors), the confidence distance measure is used as the fusion degree of data fusion, and then the confidence matrix is ​​used. The fusion matrix yields the best number of fusions for multiple sensors. The optimal fusion data of multi-sensors is obtained based on Bayesian estimation theory. The Bayesian discriminant method is essentially a pattern classifier. The process of Bayesian discriminant based on multi-sensor is actually the process of decision information fusion. Bayesian decision-making is a risk-based decision. Although decision-makers cannot control the change of objective factors, they can grasp the possible conditions of their changes and the distribution probability of each situation, and use the expected value, that is, the average situation that may occur in the future as the decision criterion. Uncertainty is the normal state of life. Bayesian decision-making is not to make decision-making problems completely risk-free, but to increase the amount of information in other ways to reduce the risk in decision-making. It can be seen that Bayesian decision making is a more practical method.
Fusion model
Information fusion models can be studied and represented in terms of functions, structures, and mathematical models. In the functional model, the fusion level of the system is the detection level, that is, the fusion on the detection decision or signal layer directly in the multi-sensor distributed detection system, which usually forms an optimization threshold according to the selected detection criteria to generate the final Detection output. For its structural model, the system adopts a parallel structure, and can also adopt a two-stage parallel structure, that is, the temperature information is first fused and then the pressure information is fused. Mathematical models are information fusion algorithms and integrated logic. There are two complementary information of pressure and temperature in the system. The fusion of complementary information reduces the ambiguity of environmental understanding due to the lack of certain environmental features, improves the integrity and correctness of the system description environment, and enhances the ability of the system to make correct decisions. Since the complementary information comes from heterogeneous sensors, they have great differences in measurement accuracy, range, and output form. Therefore, it is especially important to abstract the information of different sensors into the same expression before fusion. Here, the temperature can be converted to pressure by the ideal gas law PV = nR T and then fused. The derived formula is:
P2 = p1 + p1 ( t2 - t1 ) / 273 (1)
Where: t1 is the initial temperature; t2 is the current temperature; p1 is the initial pressure; p2 is the pressure for t2.
Let the data measured by the i-th sensor and the j-th sensor be ti and tj, and both ti and tj obey the Gaussian normal distribution. The expected E ( t ) of the measured data, the variance D ( t) formula is:
![]()
If a sensor fails during use and the situation is not considered in the algorithm, it will cause false positives or false negatives. Therefore, the multi-sensor information fusion of the system includes two contents: invalidation information elimination and effective information fusion. After eliminating the failure information, the optimal fusion data t of the multi-sensor is obtained based on the Bayes estimation theory:
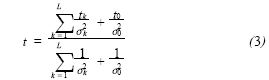
Where: tk ———the observation of the kth sensor; σk ———the standard deviation of the measured value of the kth sensor; t0 ———the mean of the observations of L valid sensors; σ0 ———L effective sensors The standard deviation of the observations.
Alarm when t is not within the given range. According to the literature, when the tire air pressure is higher than 1.2 times the reference tire pressure or lower than 25% of the reference pressure, it should be alarmed. At this time, the owner should stop to check the tire condition. If there is no abnormality, the vehicle speed will be reduced. According to industry insiders, when the tire pressure is 3 times higher than the reference pressure, the chance of a puncture is close to 100%.
system structure
Sensors and MCUs produced by different companies provide hardware assurance for the diversification of TPMS design schemes, and provide ideas for software preparation. 2 Tire pressure monitoring system structure diagram
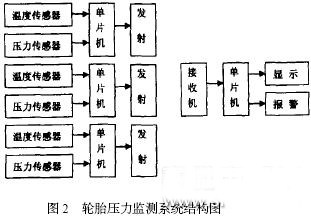
The tire pressure monitoring system consists of two parts: the measuring transmitting part and the receiving control part, as shown in Fig. 2, wherein the measuring transmitting part is responsible for accurately measuring the transmitting information, and the sampling interval is controlled by the single chip microcomputer; the receiving control part is responsible for merging and analyzing the signal, judging the Whether it is within the given range, whether it is an alarm. The measurement transmitting part uses three NPX sensors, which are connected to the transmitter correctly according to the function of each lead to complete the design of the printed circuit board (PCB). The design should minimize the size and reduce the connection. They are then inserted into the tire at 120° apart, and the internal pressure of the tire is placed between the hub and the inner tube. The receiving control section can be made into an instrument that is placed in a position that is easy for the driver to see in the cab. The alarm can be implemented by L ED lamp and audible alarm. The intensity of the light and the strength of the sound are controlled by the pressure value.
Conclusion
In the experiment, the alarm limit is 300 KPa. The expected and variance of the measured values ​​for the six sensors are:
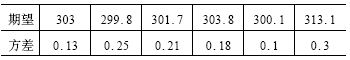
It is calculated that the data of sensor 6 is not supported by the other 5 sensors and is regarded as the failure data. The fusion results obtained after the calculation of the remaining 5 sensor data are:
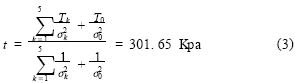
It can be seen that t is slightly larger than 300 kPa. At this time, the system should prompt the driver to be careful of the puncture. If the boost is continued, the level of the alarm is raised, and if there is a downward trend, the alarm is stopped.
There is a difficulty in the productization of the system: The data collected is too much, and the receiving control part is difficult to identify which sensor of the tire the received data is. The program is more complicated and the system structure is complicated. In order to simplify the structure, only two NPX sensors can be installed in each tire.
Mobile Power Station For Iphone,50W Portable Solar Panels,60W Portable Solar Panels,200W Portable Solar Panels
Guangzhou Fengjiu New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.flashfishbatteries.com