This article mainly elaborates on the difference between PCI bus and PXI bus. First of all, it introduces the PCI bus architecture, features and PCI bus performance. Secondly, it describes the characteristics of PXI bus. Finally, it introduces the difference between PCI bus and PXI bus.
PCI bus introductionThe PCI bus is a tree structure that is independent of the CPU bus and can operate in parallel with the CPU bus. PCI devices can be connected to PCI devices and PCI bridges. Only one PCI master device is allowed on the PCI bus. The others are PCI slave devices. The read and write operations can only be performed between master and slave devices. The data exchange needs to transit through the master device.
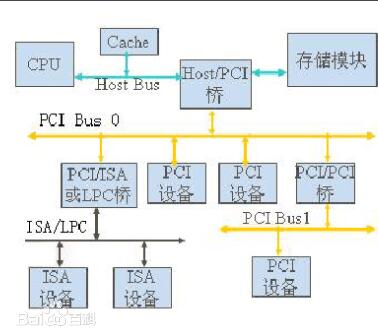
PCI bus structure diagram
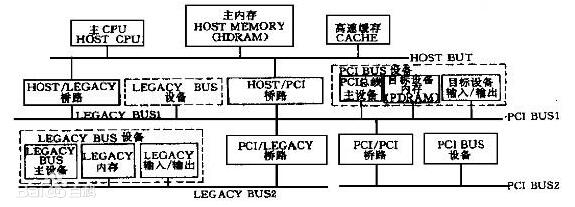
(1) High transmission rate The maximum data transmission rate is 132MB/s. When the data width is upgraded to 64 bits, the data transmission rate can reach 264MB/s. This is incomparable to other buses. It greatly eases the data I/O bottleneck, enables the function of the high-performance CPU to be fully utilized, and meets the needs of high-speed device data transmission.
(2) Multi-Bus Coexistence The use of the PCI bus allows multiple buses to co-exist in one system, allowing devices with different speeds to work together. Through the HOST-PCI bridge component chip, the CPU bus and the PCI bus are bridged; through the PCI-ISA/EISA bridge component chip, the PCI bus is bridged with the ISA/EISA bus to form a hierarchical multi-bus system. The high-speed device is removed from the ISA/EISA bus and moved to the PCI bus. The low-speed device can still be connected to the ISA/EISA bus, inheriting the original resources and expanding the compatibility of the system.
(3) The CPU-independent PCI bus is not attached to a specific processor, that is, the PCI bus supports multiple processors and new processors that will be developed in the future. When changing the types of processors, the corresponding bridging components can be replaced.
PCI bus performance(1) High transmission rate The maximum data transmission rate is 132MB/s. When the data width is upgraded to 64 bits, the data transmission rate can reach 264MB/s. This is incomparable to other buses. It greatly eases the data I/O bottleneck, enables the function of the high-performance CPU to be fully utilized, and meets the needs of high-speed device data transmission.
(2) Multi-Bus Coexistence The use of the PCI bus allows multiple buses to co-exist in one system, allowing devices with different speeds to work together. Through the HOST-PCI bridge component chip, the CPU bus and the PCI bus are bridged; through the PCI-ISA/EISA bridge component chip, the PCI bus is bridged with the ISA/EISA bus to form a hierarchical multi-bus system. The high-speed device is removed from the ISA/EISA bus and moved to the PCI bus. The low-speed device can still be connected to the ISA/EISA bus, inheriting the original resources and expanding the compatibility of the system.
(3) The CPU-independent PCI bus is not attached to a specific processor, that is, the PCI bus supports multiple processors and new processors that will be developed in the future. When changing the types of processors, the corresponding bridging components can be replaced.
(4) Automatic identification and configuration Peripheral users are easy to use.
(5) Parallel operation capability.

PXI is a rugged PC-based measurement and automation platform. PXI combines the electrical bus characteristics of PCI with the ruggedness, modularity, and Eurocard mechanical packaging of CompactPCI, and adds specialized synchronous buses and major software features. This makes it a high-performance, low-cost delivery platform for measurement and automation systems. These systems can be used in various fields such as manufacturing test, military and aviation, machine monitoring, automobile production and industrial testing.
PXI was completed in 1997 and officially launched in 1998. It is an open industry standard that has been introduced to meet the increasing demand for complex instrumentation systems. Today, PXI standards are managed by the PXI Systems Alliance (PXISA). The alliance consists of more than 60 companies that jointly promote PXI standards, ensure PXI interchangeability, and maintain PXI specifications.
Hardware Architecture The PXI system consists of three basic components: the chassis, system controller, and peripheral modules.
PXI is directly compatible with CompactPCI, so any 3U CompactPCI module can be used directly in PXI systems. In addition, Card/PCMCIA and PMC (PCI Mezzanine Card) cards can be directly inserted into PXI systems using the Carrier Module. For example, the NI PXI-8221 PC Card Carrier connects Cardbus and PCMCIA devices to a PXI system.
PXI bus features1. Newly Added Electrical Packaging Specifications
In addition to porting all of the mechanical specifications in the CompactPCI specification directly into the PXI specification, PXI has also added some requirements that CompactPCI does not have, in order to simplify system integration. As mentioned earlier, the system slot in the PXI chassis must be at the extreme left, and the master can only expand left to avoid occupying the instrument module slot. PXI also specifies that the forced cooling air flow required by the module must flow from the bottom of the module to the top. The environmental tests recommended by the PXI specification include temperature, humidity, vibration, and impact tests on all modules and test results in written form. At the same time, the PXI specification also specifies the operating and storage temperature range for all modules.
2. Interoperability with CompactPCI
One of the important features of PXI is the maintenance of interoperability with standard CompactPCI products. However, the components needed for many PXI-compatible systems may not require the full PXI bus feature. For example, users may want to use a standard CompactPCI network interface module in a PXI chassis, or use a PXI-compatible module in a standard CompactPCI chassis. In these situations, what the user needs is the basic functionality of the module rather than the complete PXI features.

In 1997, NaTIalal Instruments proposed a new solution for test and measurement applications: PXI (PCI eXtensions for InstrumentaTIon) - CompactPCI optimized for test tasks. In 1998, NI's alliance with other test equipment vendors in the PXI System Alliance brought PXI to market as an open industry standard. Today, PXI has become the standard platform for today's test, measurement, and automation applications. Its open architecture, flexibility, and cost advantages of PC technology have revolutionized the measurement and automation industry.
PXI is a modular instrument platform tailored for industrial data acquisition and automation applications. It is equipped with many professional features such as mechanical, electrical, and software. PXI takes advantage of PCI, the most popular high-speed standard for desktop computers. The PXI specification is an extension of the CompactPCI specification. CompactPCI defines a rugged, industrial-strength PCI bus architecture that provides excellent mechanical integrity with easy hardware handling.
Therefore, PXI products have higher level and more stringent environmental consistency indicators, which meet the extreme conditions of vibration, impact, temperature, and humidity in industrial environments. PXI has imposed environmental performance tests and active cooling devices on the CompactPCI's mechanical specifications to simplify system integration and ensure interoperability between products from different vendors. In addition, PXI also complements the timing and triggering features specific to measurement and automation systems based on the high-speed PCI bus.
In general, PXI is a rugged, modular instrument platform that offers computer-based, high-performance, standardized measurement and automation solutions. Provides much better performance than the original system architecture at a reasonable price. PXI users naturally enjoy many advantages such as cheap, easy-to-use, flexible PC technology; open industry standards and full interoperability with CompactPCI products.
Solar Pv Test Equipment,Photovoltaic Testing Tools,Solar Iv Tester,Solar Pv Testing Kit
Sowell Electric CO., LTD. , https://www.sowellsolar.com