1. IPTV business requirements
The IPTV service imposes the following requirements on the access network:
â— High network bandwidth and available bandwidth of subscriber lines;
â— Support QoS, provide bandwidth guarantee and priority scheduling mechanism of video stream to ensure the distribution of video stream;
â— The access network equipment needs to support multicast, and quickly process the user's multicast request;
â— Support multi-service, terminal access and management;
â— User access authentication, user multicast rights management;
â— High network reliability and networking redundancy.
2. Multi-edge mode supports IPTV services
The multi-edge mode suitable for multi-service development can better support the network requirements of IPTV services, as shown in Figure 1. In multi-edge mode: high-speed Internet access is controlled by an IP edge access and BRAS; IPTV services are directed to the middleware platform through another IP edge; VoIP services and other services are directed to softswitch or related platforms through another IP edge; Broadcast replication and user control are completed in DSLAM; high-speed Internet services use PPPoE authentication to fully protect existing network investment; IPTV / NGN business network layer authentication is completed through DHCP OpTIon 82. Multiple ATM PVCs or / and multiple Ethernet VLANs respectively carry different services, that is, the services are logically differentiated and carried at the access layer. At present, European operators and some domestic operators have already carried IPTV services on networks that deploy this business model. Multi-edge is a network architecture based on multi-service bearing, which can smoothly upgrade and carry various services to protect the existing investment.
3. Service separation technology in the access network
Under the multi-edge architecture, how to complete the separation of users' various business data in the access network has put forward new requirements for the access equipment DSLAM. There are currently multiple PVC and single PVC solutions in the access equipment.
(1) Multiple PVC solutions
The multi-PVC scheme is shown in Figure 2. In this solution, each port of the access equipment DSLAM should support multiple PVCs. The untag data service streams sent by different user terminals are respectively carried by different PVCs; PVC to VLAN mapping should be supported, and the service streams of different PVCs are mapped to different service VLANs respectively, corresponding to S-VLAN1 and S- in Figure 2 VLAN2; In the VLAN Stacking application mode, S-VLAN is used to identify services, and C-VLAN is used to identify users. DSLAM completes the mapping of PVC to VLAN. The service flows of different VCs are mapped to different S-VLANs, corresponding to S-VLAN1 and S-VLAN2 in Figure 2; the service flows of different users use different C-VLAN identifiers, corresponding to C-VLAN1 and C-VLAN2 in the figure And C-VLAN3.
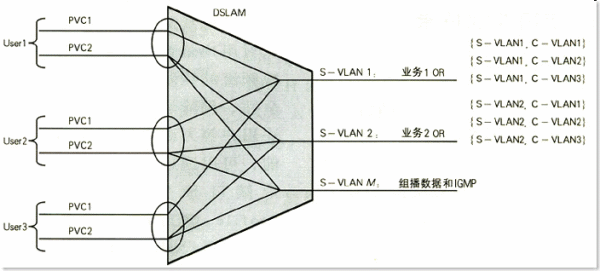
Multi-PVC scheme
(2) Single PVC solution
The single PVC scheme is shown in Figure 3. In this solution, the access equipment DSLAM should support each DSL port to use a single PVC (or PVC-free packet interface) to carry different services; DSLAM maps PPPoE and IPoE messages to different services according to the Ethernet type of the message VLAN, corresponding to S-VLAN1 and S-VLAN2 in Figure 3 (N: 1 mapping, that is, the same service of different users is mapped to the same service VLAN). In addition to distinguishing service data on a single PVC based on the Ethernet type of the data packet, DSLAM equipment can also differentiate services based on VLAN tags, but this places higher requirements on customer premises equipment (CPE).
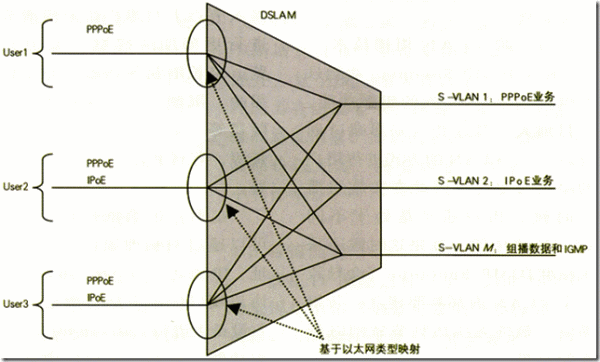
Single PVC scheme
In contrast, the multi-PVC solution is more mature, and the current equipment support is better. Carrying different services with different PVCs has advantages in QoS guarantee, service management and service monitoring.
4. Multicast control technology
IP multicast technology effectively solves the problems of single-point multi-point reception and multi-point multi-point reception, and realizes efficient data transmission from point to multipoint in the IP network, which can effectively save network bandwidth and reduce network load. The basic IGMP Snooping / proxy function can solve the problem of multicast layer 2 flooding. In the IPTV service environment, cross-VLAN multicast technology, enhanced multicast control technology, preview function, and call details can be effectively Realize the management of user multicast services.
(1) Cross-VLAN multicast technology
The standard IGMP Snooping function only provides the multicast function in the same VLAN, and most operators currently use port division 802.1q VLAN to isolate and locate users. Therefore, when implementing multicast, users are usually in different VLANs. Among them, if the standard IGMP Snooping is also used at this time, it will cause a multicast stream to be established inside each VLAN, and ultimately the effect of saving network bandwidth cannot be achieved.
Using cross-VLAN multicast technology can solve this problem well. For example, a multicast program source A is delivered to DSLAM from VLAN 100 on the network side. For user 1 who belongs to VLAN 1 and user 2 who belongs to VLAN 2, when they order program A, DSLAM will transfer the data of program A. The flow is copied from VLAN 100 to User 1 and User 2. For program A, there is always only one stream between the DSLAM and the upper-layer equipment, which achieves the purpose of saving bandwidth to the greatest extent. Therefore, implementing cross-VLAN multicast in the access network is an indispensable function of DSLAM or access node.
(2) Multicast access control
IGMP itself does not have a method to control whether a user can join a certain multicast group, and since the multicast data stream is replicated at the access node, whether the user is allowed to obtain a certain multicast video stream at the access node Control is especially important for the security of video data, protection of the interests of operators, and prevention of illegal users. At present, personalized profiles can be pre-set on the user port through the device management function to set access rights for a specific group or group of multicast programs, allow or prohibit users from joining, control multicast services, and prevent illegal users from occupying network resources . Through similar functions, you can also control users' access to multicast programs on the access node, such as controllable preview, parental restriction, etc., for specific users, limit the programs and the number of programs they can watch, which is effective Protecting the resources of operators is conducive to the healthy development of IPTV services.
In terms of the user's legality check, you can select the binding of the combination of physical port, MAC address, IP address, VLAN, protocol type and protocol port to perform AnTI-spoofing anti-spoofing function on the access device, thereby achieving internal network Security management to prevent IP address conflicts, etc.
In terms of preventing the proliferation of illegal multicast sources, you can prevent illegal multicast video data from flowing into the network by implementing a method of blocking upstream multicast data on the access node.
(3) User call detail list function
User call detail list is an indispensable function of IPTV service operation. DSLAM should be able to record users' on-demand behavior and related information in detail, and synchronize with the data of IPTV service platform. The user call detail list provides strong data support for business billing, viewing statistics, and user behavior analysis.
5. Performance and QoS technology of access network equipment
In order to meet the user's needs for video service picture quality and rapid access to information, it is usually necessary to access the network to achieve bandwidth requirements of more than 2 Mbit / s per user port, non-blocking forwarding, and make a millisecond quick response to user join requests. Under the multi-service, multi-PVC scheme, at least four or more PVCs per port can be achieved. The access layer can support simultaneous replication of multicast streams of at least 1 k. In terms of QoS service quality assurance, the access network equipment is required to have DiffSev capability, support 802.1p priority label identification and mapping, support 4 priority queues per port, and data flow supervision and shaping technology.
6. Conclusion
In summary, the access network is the first network directly facing users. Due to the large number of users, complicated access methods, and high security requirements, when supporting IPTV services, in addition to the need for a substantial increase in bandwidth In addition to meeting the needs of video services, support for multi-edge architectures, service separation technologies, multiple enhanced multicast control technologies, and QoS-related technologies will be the key to better carrying IPTV services.
Iron Battery,Nife Batteries Australia,Nife Battery 600Ah For Asutralia,Ni-Fe Battery 450~600Ah
Henan Xintaihang Power Source Co.,Ltd , https://www.taihangbattery.com