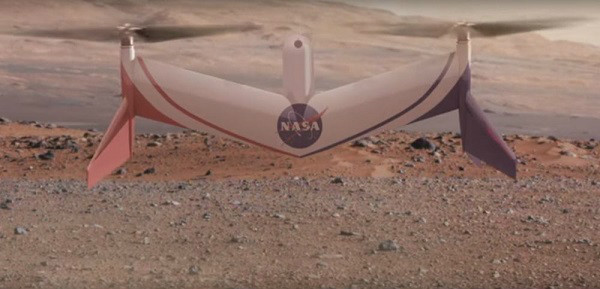
: Mars is the planet closest to Earth. Human exploration of Mars has never stopped. However, the problem is that the current exploration of Mars still remains at the level of the Mars Rover, and it is impossible to get a more detailed picture of Mars, and NASA has once again opened a brain hole. They intend to use autonomous drones to cooperate with the Rover. Unexplored exploration missions.







The GPS Antenna, also known as the Global Positioning System Antenna, is a crucial component in modern navigation and positioning systems. It serves as the primary interface between GPS satellites and GPS receivers, enabling accurate and reliable location tracking. Below is a detailed introduction to GPS Antennas, highlighting their key features, types, applications, and technical specifications, emphasizing the importance of their design and placement for optimal signal reception and performance.
Key Features:
Signal Reception: GPS Antennas are designed to efficiently receive signals from GPS satellites orbiting the Earth. These signals, transmitted at frequencies such as 1575.42 MHz (L1) and 1228 MHz (L2), are captured by the antenna and converted into electrical signals for processing.
Precision and Accuracy: The antenna's design and materials contribute to its ability to receive signals with high precision and accuracy. This ensures that the GPS receiver can determine the vehicle's or device's position with minimal error.
Multi-Band Support: Some GPS Antennas support multiple frequency bands, allowing them to receive signals from different constellations of satellites, enhancing their versatility and reliability.
Durability: GPS Antennas are typically built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to weather elements, vibrations, and other potential stressors.
Types:
Passive Antennas: These antennas do not contain any active electronic components, relying solely on the antenna's design to capture and transmit signals. They are often simpler and lighter than active antennas but may have lower gain and sensitivity.
Active Antennas: Also known as GPS Active Antennas, these devices incorporate low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) to boost the received signal strength. This improves their sensitivity and performance, especially in environments with weak signals or interference.
External vs. Internal Antennas: External GPS Antennas are typically mounted on the exterior of a vehicle or structure, providing better line-of-sight to the sky and thus better signal reception. Internal antennas, on the other hand, are integrated into the device or vehicle's interior, offering a more streamlined design but potentially compromising signal reception.
Key Features:
Signal Reception: GPS Antennas are designed to efficiently receive signals from GPS satellites orbiting the Earth. These signals, transmitted at frequencies such as 1575.42 MHz (L1) and 1228 MHz (L2), are captured by the antenna and converted into electrical signals for processing.
Precision and Accuracy: The antenna's design and materials contribute to its ability to receive signals with high precision and accuracy. This ensures that the GPS receiver can determine the vehicle's or device's position with minimal error.
Multi-Band Support: Some GPS Antennas support multiple frequency bands, allowing them to receive signals from different constellations of satellites, enhancing their versatility and reliability.
Durability: GPS Antennas are typically built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to weather elements, vibrations, and other potential stressors.
Types:
Passive Antennas: These antennas do not contain any active electronic components, relying solely on the antenna's design to capture and transmit signals. They are often simpler and lighter than active antennas but may have lower gain and sensitivity.
Active Antennas: Also known as GPS Active Antennas, these devices incorporate low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) to boost the received signal strength. This improves their sensitivity and performance, especially in environments with weak signals or interference.
External vs. Internal Antennas: External GPS Antennas are typically mounted on the exterior of a vehicle or structure, providing better line-of-sight to the sky and thus better signal reception. Internal antennas, on the other hand, are integrated into the device or vehicle's interior, offering a more streamlined design but potentially compromising signal reception.

gps glonass antenna,gps active antenna,marine gps antenna,gnss gps antenna,GPS Antennas
Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.yetnorson.com