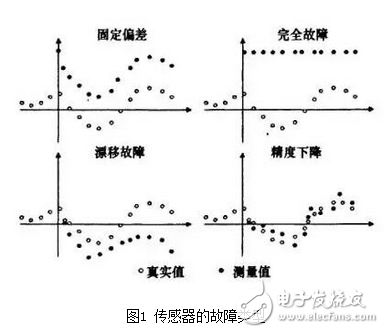
Sensor faults mainly include four types: complete failure fault, fixed deviation fault, drift deviation fault and precision drop. As shown in Figure 1.
Among them, the failure fault refers to the sudden failure of the sensor measurement, and the measured value is always a certain constant; the deviation fault mainly refers to a type of fault where the measured value of the sensor differs from the true value by a constant constant, as can be seen from the figure, the fault is faulty. Measurements are parallel to fault-free measurements;
Drift fault is a type of fault that occurs when the difference between the measured value of the sensor and the true value is increased at any time.
The decrease in accuracy means that the measurement capability of the sensor is deteriorated and the accuracy is lowered. When the accuracy level is lowered, the average value of the measurement does not change, but the variance of the measurement changes.
Fixed deviation faults and drift faults are faults that are not easy to find. In the process of fault occurrence, a series of unpredictable problems will occur, which will make the control system not function properly for a long time.
Sensor fault classification
1, according to the degree of sensor failure classification
According to the degree of sensor failure, it can be divided into hard fault and soft fault.
A hard fault generally refers to a fault caused by structural damage. Generally, the amplitude is large and the change is sudden. The soft fault generally refers to the variation of the characteristic, the amplitude is small, and the change is slow.
A hard fault is also called a complete fault. When the fault is completely faulty, the measured value does not change with the actual change, and a certain reading is always maintained. Usually this constant value is typically zero or maximum reading. The fault measurement is roughly a horizontal straight line.
Soft faults include data skew, drift, and reduced accuracy levels. Soft faults are relatively small and difficult to find. Therefore, in a sense, soft fault hazards are more harmful than hard faults, and their harm has gradually attracted people's attention.
2, according to the performance of the fault classification
According to the performance of faults, it can be divided into intermittent faults and permanent faults.
Intermittent faults are good or bad; after a permanent fault fails, it can no longer be restored.
3. Classification according to the process of fault occurrence and development
According to the process of fault occurrence and development, it can be divided into sudden fault and slow fault.
The rate of change of the sudden fault signal is large; the rate of change of the slowly varying fault signal is small.
4, according to the cause of the failure
According to the cause of the fault, it can be divided into deviation fault, impact fault, open fault, drift fault, short circuit fault, periodic interference, and nonlinear dead zone fault.
The cause of the fault fault is: bias current or bias voltage;
The cause of the failure of the impact fault is: random interference in the power supply and ground, surge, spark discharge, burrs in the D/A converter, etc.;
The cause of the open circuit fault: the signal line is broken, the chip pin is not connected, etc.;
The cause of the drift fault: warm, etc.;
The cause of the short-circuit fault: bridge corrosion caused by pollution, short circuit of the line, etc.;
Causes of periodic interference: 50 Hz interference from the power supply;
The cause of the failure of the nonlinear dead zone fault: the amplifier is saturated, contains nonlinear links, and so on.
In addition, from the perspective of modeling and simulation, it can be divided into multiplicative faults and additive faults. For the bias fault, a constant or random small signal is added to the original signal; for the impulse interference, a pulse signal can be superimposed on the original signal; for the short circuit fault, the signal is close to zero; for the open circuit fault, the signal is close to the sensor output maximum value; Drift failure, the signal is offset from the original signal at a certain rate; periodically interferes with the fault, and the signal of a certain frequency is superimposed on the original signal.
6.2Mm Ribbon Connector,Wire-To-Wire Connector,Ket Connectors,6.2Mm Ribbon Connectors
YUEQING WEIMAI ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD , https://www.wmconnector.com