Just a few months ago, the remote medical kiosk operator HealthSpot, which announced a high-profile cooperation with Samsung, stopped operating at the end of 2015 without warning and officially filed for bankruptcy liquidation in early 2016.
According to the bankruptcy liquidation document, HealthSpot suddenly collapsed because of the depletion of its cash flow. The cash before the bankruptcy was only less than $90,000 and it was no longer possible to continue operations. According to the document, HealthSpot has only $1.1 million in revenue in the past three years, of which $600,000 occurred in 2015. HealthSpot's assets are $5.2 million, of which $3.5 million is inventories, including 137 telemedicine kiosks. Its liabilities are as high as $23.3 million, of which $10 million is from convertible bonds of the third largest telecom operator Cox CommunicaTIons and $6 million from Xerox.
The failure of HealthSpot has had little impact on the industry, but it is still worth looking for the reasons for its failure and analyzing future trends. The telemedicine kiosk is a new medical service model in the United States in recent years. It is mainly placed in retail channels such as supermarket pharmacies. Users can directly consult doctors and get prescriptions through this device. The telemedicine kiosk hopes to have a large passenger flow. Retail channels to drive their own development.

However, from the failure of HealthSpot, this passive mode of access is extremely challenging, and it is impossible to truly acquire enough users to support its own development. Even with a $23 million venture capital in 2014, HealthSpot quickly burned out and had to close down. This can be seen in comparison with another old telemedicine service provider, higi.
Higi has completed the deployment of telemedicine kiosks in nearly 10,000 retail channels across the United States, and in January 2016 just announced the latest round of $40 million in investment. Higi's customer acquisition model is not only from the retail channel, but also from insurance and pharmaceutical companies and other partners who are willing to pay more. Moreover, higi has also developed an online health management platform. Through this platform, it cooperates with offline layouts, and encourages users to collect and share their health data through incentive programs, further enhancing the interaction between the platform and users, thus promoting the entire chain. The perfection, and the telemedicine kiosk is only part of its overall service, which greatly improves the problem of single and lack of interaction.
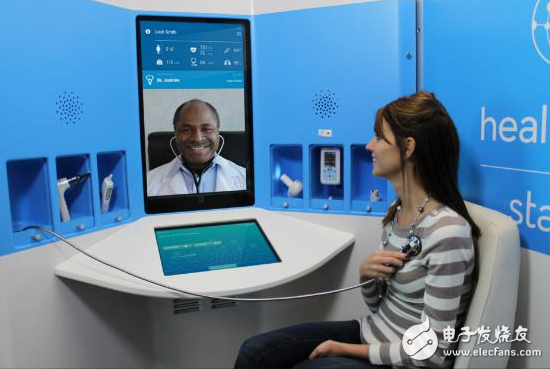
HealthSpot's "Remote Medical Kiosk" can no longer see such a warm picture.
Of course, the collapse of HealthSpot still reveals the shortcomings of telemedicine itself. First of all, the needs of both doctors and patients are still not strong. According to a survey conducted by the National Association of Family Physicians in the American Family Doctors Journal in 2016, although up to 78% of doctors indicated that they are willing to use telemedicine, only 15% of family doctors used telemedicine in 2014 to The patient provides services. Family doctors believe that the main obstacles to telemedicine are lack of training, inability to obtain insurance claims, equipment costs, and possible liability. Another survey in 2015 showed that only 9% of patients would actually use a remote consultation. This can also be seen from Teladoc, the first remote consultation company listed in the United States. According to estimates, although Teladoc has a large membership base, the actual number of clinics is relatively limited, and the average may be around 3%.

Second, the number of pay-per-view remote consultation revenues is not optimistic enough to support a company's individual development. HealthSpot has only $600,000 in revenues for the best revenues in 2015. Compared to Teladoc's 2015 survey of 575,000, it can only earn about $10 million in actual medical visits. HealthSpot's most optimistic annual consultation It is also about 30,000 times, spread to 137 telemedicine kiosks, and the number of occurrences per day can only be maintained once. As the fastest-growing remote consultation company, Teladoc relies mainly on membership fees to sustain growth, and HealthSpot is more difficult to obtain the consultations and corresponding revenues needed to sustain its growth.
Finally, offline retail basic medical care is undergoing large-scale development and has become the most powerful competitor for remote consultation. Since users still have doubts about online consultations, the retail channel-based consultation is more popular. Since a large number of retail channels begin to distribute clinics, they will only hand over the poor stores to the telemedicine booths, and will be better. Leaving it to your own clinic, this further squeezes the space for the development of telemedicine kiosks. For example, Wal-Mart's rapid clinic visit fee is $40/time, and Teladoc has no advantage over this price. And users who buy insurance can get services at retail clinics for only $4, a price that far defeats telemedicine.

Therefore, from the collapse of HealthSpot, even in the market environment that is greatly promoted by the United States, the development of telemedicine still faces many challenges and squeeze from offline. However, in the next few years, the development of telemedicine will continue to maintain rapid growth, but the growth of the border and overall market size will be greatly affected by the user's willingness and the development of offline basic medical care.
UCOAX Custom Made Link Cable Compatible for Oculus Quest 2, Fast Charging & PC Data Transfer USB C 3.2 Gen1 Cable for VR Headset and Gaming PC 16FT(5M)
Compatible for Oculus Quest 2: KRX link cable has perfect compatibility for oculus quest 2, so you can enjoy your gaming time happily
Flexiable lengths of link cables for you to choose. Choose the right one according to your needs
High-speed transmission & Fast Charging: The 3A current allows you to charge quickly while playing, maintaining stable and high-speed data transmission
USB C cable version: KRX USB C cable compatible with usb 3.0/3.1 gen1/3.2 gen1
90 Degree angle metal head design: The 90-degree USB C design makes you more stable and not easily damaged when playing
Virtual Reality Link Cable,Oculus 2 Cable,Vr To Pc Cable,Virtual Reality Link Cable Device
UCOAX , https://www.jsucoax.com