[Source: "High-tech LED - Technology and Applications" February issue Zhu Zhaohui]
I. Introduction
High temperature operating environments are the biggest threat to LEDs and other silicon-based semiconductors. With the rapid development of the electronics industry, the size of electronic products is getting smaller and smaller, and the power density is getting larger and larger. Solving the heat dissipation problem is a huge challenge to the electronics industry design. The use of a heat-dissipating metal substrate is undoubtedly one of the effective means to solve the heat dissipation problem. In order to break through the existing technical bottleneck of heat dissipation, it is necessary to introduce a metal-based circuit board with high thermal conductivity and high heat dissipation.
Second, the current status and application of metal substrates
1. Metal substrate application
The most widely used aluminum-based copper clad plate in metal substrates Compared with the conventional FR-4, the aluminum substrate can minimize the thermal resistance and make the substrate have excellent thermal conductivity; compared with the thick film ceramic circuit, its The mechanical properties are extremely excellent. In addition, aluminum substrates have the following unique advantages:

Meet the requirements of RoHs, green products. 
Extremely efficient processing of thermal diffusion in circuit design.
Reduce module operating temperature, extend service life, and increase power density and reliability.
Reduce assembly of heat sinks and other hardware (including thermal interface materials), reduce module size, and reduce hardware and assembly costs. 
Replace the fragile ceramic substrate for better mechanical durability.
Mainly used in terminal products for electrical appliances with heat dissipation requirements, such as high-brightness LEDs, output amplifiers, equalization amplifiers, preamplifiers, transistor pedestals, solid state relays, power supply units, power supplies, DC transformers, automotive electrical modules, etc. .
2. Metal heat conduction parameters and related metal substrate materials
Heat transfer coefficient (W/mK): refers to the material that is 1mm thick under stable heat transfer conditions. The temperature difference between the two sides is 1 degree (K, °C), and the heat transferred through the area of ​​1 square meter in one hour, the unit It is watt/meter? (W/m?K, where K can be replaced by °C). Part of the metal conduction coefficient is shown in Table 1:
For more information, please refer to the February issue of "High-tech LED-Technology and Applications" magazine.
I. Introduction
High temperature operating environments are the biggest threat to LEDs and other silicon-based semiconductors. With the rapid development of the electronics industry, the size of electronic products is getting smaller and smaller, and the power density is getting larger and larger. Solving the heat dissipation problem is a huge challenge to the electronics industry design. The use of a heat-dissipating metal substrate is undoubtedly one of the effective means to solve the heat dissipation problem. In order to break through the existing technical bottleneck of heat dissipation, it is necessary to introduce a metal-based circuit board with high thermal conductivity and high heat dissipation.
Second, the current status and application of metal substrates
1. Metal substrate application
The most widely used aluminum-based copper clad plate in metal substrates Compared with the conventional FR-4, the aluminum substrate can minimize the thermal resistance and make the substrate have excellent thermal conductivity; compared with the thick film ceramic circuit, its The mechanical properties are extremely excellent. In addition, aluminum substrates have the following unique advantages:

Meet the requirements of RoHs, green products. 
Extremely efficient processing of thermal diffusion in circuit design.
Reduce module operating temperature, extend service life, and increase power density and reliability.
Reduce assembly of heat sinks and other hardware (including thermal interface materials), reduce module size, and reduce hardware and assembly costs. 
Replace the fragile ceramic substrate for better mechanical durability.
Mainly used in terminal products for electrical appliances with heat dissipation requirements, such as high-brightness LEDs, output amplifiers, equalization amplifiers, preamplifiers, transistor pedestals, solid state relays, power supply units, power supplies, DC transformers, automotive electrical modules, etc. .
2. Metal heat conduction parameters and related metal substrate materials
Heat transfer coefficient (W/mK): refers to the material that is 1mm thick under stable heat transfer conditions. The temperature difference between the two sides is 1 degree (K, °C), and the heat transferred through the area of ​​1 square meter in one hour, the unit It is watt/meter? (W/m?K, where K can be replaced by °C). Part of the metal conduction coefficient is shown in Table 1:
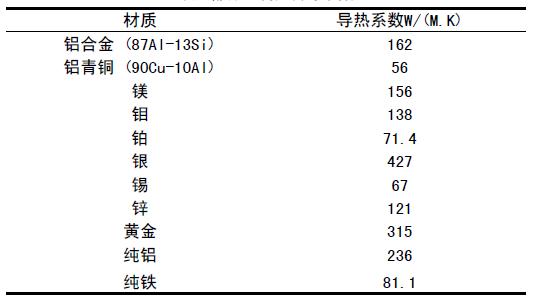
For more information, please refer to the February issue of "High-tech LED-Technology and Applications" magazine.

Directly Supply Imported Stainless Steel Rod,SUS304 Imported Stainless Steel Rod, 316 Imported Stainless Steel Rod
ShenZhen Haofa Metal Precision Parts Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.haofametal.com