Every time you want to help your mobile phone, computer, or other various electrical appliances, you must always pick up a charging cable. There are more charging cables, and you often get the wrong ones. It is very troublesome. Fortunately, more and more electronic products are now using the "wireless charging" technology! As long as you elegantly put your phone on a small, cup-like thing, you can easily charge it without wiring. What is the principle behind such a powerful technology? Let us explore the mystery together.

Electrical and magnetic interaction
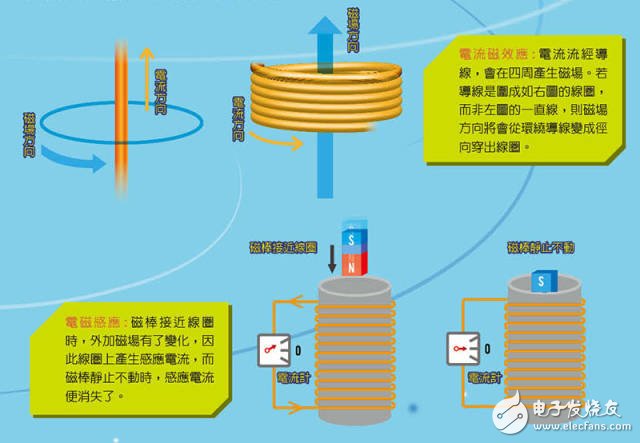
The wireless charging that is commonly seen uses the principles of "current magnetic effect" and "electromagnetic induction". In 1819, the Danish scientist Erst observed that if there was a current on a wire, a magnetic field would be generated around it, which would deflect the north arrow. Later generations further discovered that the wire is enclosed in a ring shape, even wound into a coil, and the generated magnetic field will be stronger and more concentrated. This is called "current magnetic effect."
As for electromagnetic induction, it was discovered by Faraday in 1831. When a magnet or other source of magnetic field is placed close to a coil that has no current, an "inductive current" is generated on the coil, called "electromagnetic induction." It is worth noting that the condition of electromagnetic induction is that the magnetic field should be "changed", for example, the magnet is getting closer and closer (more and more away from it). If the applied magnetic field remains constant, there will be no induced current.
In summary, the current magnetic effect is that the flow of current generates a magnetic field around, and the electromagnetic induction is a constantly changing external magnetic field that causes the coil to generate an induced current.
Use electromagnetic induction to charge
These two physical phenomena can be used simultaneously to perform wireless charging. Current wireless charging devices include a "charging stand", which is actually a coil. When the charging stand is connected to the household plug, a magnetic field is generated around the coil due to the current magnetic effect. The electronic product to be charged also has a coil inside. When it is close to the charging stand, the magnetic field of the charging stand will generate an induced current on the coil of the electronic product through electromagnetic induction. The induction current is directed to the battery, which completes the wireless charging between the charging stand and the electronic product.
You may ask, is the magnetic field not changed to have electromagnetic induction? However, the distance between the charging stand and the charged object remains the same, so why is there electromagnetic induction? It turns out that the electricity flowing out of the household outlet is "alternating current", that is to say, the direction of the current is constantly changing alternately, and then the flow follows, and the flow is reversed for a while. Because of this, the magnetic field generated by the charging socket coil is constantly changing direction, and does not remain unchanged, which is in accordance with the conditions of electromagnetic induction.
Recently, more and more smartphones and tablets have begun to provide wireless charging functions, but unfortunately, when charging, as long as they are a little farther away from the charging stand, the charging efficiency will drop significantly. Even with the latest technology, the charging distance can't exceed 5 cm. In fact, most mobile devices that can be wirelessly charged are completely flat on the charging stand, and can imagine the wireless with the charging. There is still some difference in charging.
Use resonance to lengthen the charging distance
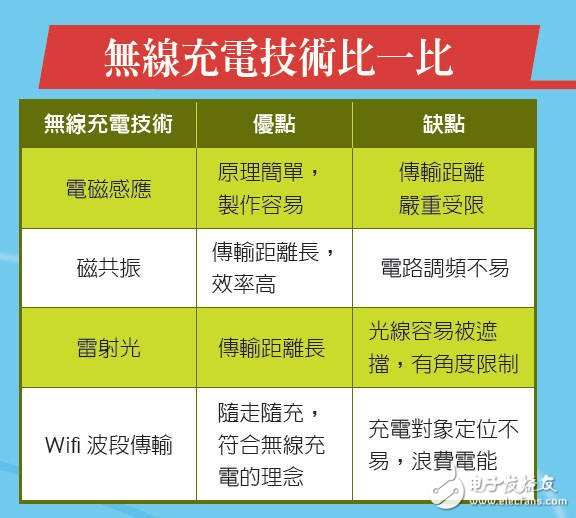
In order to increase the distance and charging efficiency of wireless charging, scientists are trying to use the principle of "magnetic resonance" for wireless charging. Add some special components such as capacitors and inductors to the circuit. When properly connected, a "resonant circuit" will be formed. This is like the tuning tool that the instrument line must have—the tuning fork. Tap the tuning fork once, it can continue to vibrate for a period of time. Similarly, the resonant circuit is briefly energized, and the signal is generated in the circuit for a period of time.
Tuning forks have the interesting physical properties of "resonance." Each tuning fork has its own vocal frequency. When a tuning fork vibrates, if there is another tuning fork with the same vocal frequency nearby, even if it is not directly hit, it will vibrate. The resonance of the tuning fork can be said to achieve the transfer of energy. The resonant circuit can also resonate. Two resonant circuits with the same vibration frequency are put together. When one of them begins to oscillate due to energization, the other circuit will also oscillate and “automatically†generate current, and the electric energy is transmitted through the space. . This phenomenon is called "magnetic resonance" and is used for wireless charging. It can make the charging distance reach several meters and the efficiency is also improved. The only difficulty is that it is not easy to adjust the two circuits to exactly the same frequency for a period of time.
In addition to magnetic resonance, some scientists try to charge with the light energy of laser light, or even transmit it through the radio frequency band similar to the Wifi network of the home. I hope that the breakthrough of these technologies will make us more convenient in charging in the future!
Features of fishing rod sleeve
Materia l: PET
Diameter: custom
Length: custom
Expanding Ratio: 200%
Color: colorful
Melting point: 230 °C ± 5
Tinting strength: 100 ± 5 °C
Fireproofing grade: UL94V-2
Temperature endurance: -50 °C~ +150 °C
PET sleeve quality: UL,SGS,Rohs,Reach,etc.
1. Light weight & Flexible & Insulation & UV Resistant & Decoration & Flame-retardant & Durable abrasion resistance & Resistant to chemical degradation, in a wide range of industrial applications.
2. Braided of 0.25mm / 0.2mm Pet monofilament.
3. The open weave construction allows an easy installation on a bundle of hoses and cables, even if some with bulky or large connectors.
Other Kinds Of Sleeves,Fishing Rod Cover,Special Sleeve ,Fish Handle Cover,Fishiing Handle Sleeve
Shenzhen Huiyunhai Tech.Co.,Ltd , https://www.hyhbraidedsleeve.com