According to statistics provided by the World Health Organization, there are about 1.2 million people killed in car accidents every year in the world, and the number of injured is about 50 million. In 1990, the number of deaths was only 9th among car accidents. Some agencies predict that by 2020, if the safety measures of the car traffic system are not significantly improved, the number of deaths caused by car accidents will rise to the third place of death. .
This article refers to the address: http://
In order to improve the safety and intelligence of the transportation system, the system concept of intelligent transportation is gradually emerging. Intelligent transportation can utilize the new generation of communication networks and data processing capabilities to improve the overall efficiency of the transportation system, reduce energy consumption, and increase the safety and convenience of transportation. In the near future, the development of intelligent transportation systems will mainly focus on the field of intelligent highway transportation systems, also known as the Internet of Vehicles.
Application scenario
There are many application scenarios for the Internet of Vehicles, some of which are already seen now, and some are predictive. Undoubtedly, improving traffic safety is the most important application, including: First, when vehicles are found to be dangerous, such as when there are obstacles in front, they can promptly remind other vehicles; Second, the vehicle can inform other vehicles of their own direction. To help drivers of other vehicles to make more accurate judgments; Third, to alert other vehicles when approaching intersections; 4. When prompted to leave the expressway, prompt to other vehicles; 5. Early warning of temporary/sudden parking; Reminder when the line; seven, the accident report; eight, the car driver reminds the roadside pedestrians / cyclists.
In terms of traffic management, the Internet of Vehicles can help clear traffic and take effective measures against congestion in real time. Management can flexibly implement traffic rules based on specific conditions, such as adjustable speed limits, variable signal periods and flash sequences, automatic traffic control at intersections, and ambulance/fire truck/police lanes.
In terms of driver assistance, intelligent transportation can provide automatic parking, navigation status, road sign recognition and the like. For police and other law enforcement agencies, the Internet of Vehicles helps monitoring, speeding reminders, restricted area management, and enforcement of orders. Through electronic payment, the Internet of Vehicles makes the collection of tolls/parking fees more convenient and convenient, to reduce the congestion of traffic flow to a certain extent, and to reduce the low-speed rear-end collisions that often occur near toll stations.
With the rapid development of automotive electronics, the computing power of the vehicle itself has also been greatly improved. As long as the Internet of Vehicles can provide a large amount of road information, according to the electronic map and previous data on the vehicle, the car's own system can pass complex optimization algorithms. Plan the best path and, in some cases, autopilot on the highway. For example, a large truck fleet has only the driver in the foremost car. There are only a few sensors and communicators in the rear truck to contact the first car, update the information in time, and adapt to the road conditions to achieve reasonable driving.
Technical direction
V2V, or extended to V2X, refers to the communication system between cars and vehicles, or between cars and roadside pedestrians/cyclists. Such systems are the so-called Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs), which belong to a mobile ad-hoc network (MANETs). In this network, each car that enters the network can become a network node with mobility. Each node works with other nodes to reduce dead zones and avoid accidents.
At present, the most important purpose of the Internet of Vehicles is to improve traffic safety. The demand is concentrated in: first, low latency, end-to-end delay within 5ms; second, high reliability, error rate below 99.999%, and When the vehicle is congested and a large number of nodes share limited spectrum resources, the reliability of the transmission can still be guaranteed. Third, it may be necessary to support high-speed mobile. Considering the relative movement between cars, the maximum relative speed can reach 500km/h; The data packet can carry at least 1600 bytes of information data.
The development of the Internet of Vehicles is cross-industry and involves many technologies. Here we focus on the close relationship between wireless communication and systems, starting from the physical layer and the network layer.
Existing technology
Currently, a protocol framework consisting of IEEE 802.11p and IEEE 1609 can accomplish some of the most basic functions of the Internet of Vehicles. IEEE 802.11p is a version of the IEEE 802.11 family that is specifically "customized" for the Internet of Vehicles. In this way, the key technology of WiFi, IEEE802.11 technology, is being extended to the V2X application of the Internet of Vehicles through 802.11p. IEEE802.11p inherits most of the physical frame structure design of WiFi, including OFDM transmission, and basic media access control (MAC) layer protocol. Currently, it supports 5MHz/10MHz/20MHz bandwidth. In the US, the frequency band is 5850MHz~5925MHz. The bandwidth is 10MHz, a total of seven, two of which can only be used by the public security department. Compared with the general cellular network, IEEE802.11p can cover a radius of less than 500m, which is called short-distance communication (DSRC) technology. At the same time, the clock broadcasting and enhanced channel suppression technology are introduced in the IEEE802.11p protocol to strengthen the physical layer of the car networking. Among them, the clock broadcasting technology can help the node keep in sync with the common time reference; and the channel suppression purpose is to improve the resistance of the receiver to the out-of-band interference of about 5 GHz.
Due to the rapid mobility of the vehicle, the communication link between the vehicle and the roadside network infrastructure is also temporary, that is, only in a short period of time. So this link must establish a connection and send data in a very short time. The cumbersome connection authentication process in IEEE 802.11 technology takes too long to be used in the Internet of Vehicles. To this end, IEEE 1609 fills the gap in the high-level agreement and forms a complete protocol stack. IEEE1609 includes four sub-protocols, of which IEEE1609.1 defines resource management, linking the remote application layer with the current vehicle; IEEE1609.2 provides security services for application layer and management information; IEEE1609.3 is IEEE802.11p network Layer; in general, IEEE 1609.4 can handle multi-channel communication.
In addition to short-range communication using IEEE802.11p, communication technologies for longer distances, such as WiMAX (IEEE 802.16), GSM or 3G/4G, have been considered as potential vehicle networking technologies. But these technologies require extensive and costly infrastructure deployments and technological improvements specific to the needs of the Internet of Vehicles.
In the underlying network of the Internet of Vehicles, nodes are mainly divided into two categories: Vehicular on-board units and road-side units. The roadside unit acts as an anchor point in the WiFi network to provide communication with the underlying network. If necessary, the roadside unit is responsible for assigning a transmission channel to the onboard unit. The roadside unit needs to periodically transmit a "beacon" signal on the control channel for the onboard unit to monitor and recognize. This process and the physical layer signal are somewhat different from WiFi. There is also a special node, usually placed in the police, fire or emergency vehicles in the emergency scene. Although they are on-board units, they also have many functions of the roadside unit.
Future technical direction
â— Reduce latency technology
In order to better meet the requirements of low latency, the physical networking layer protocol of the car network needs to rely on the adaptation of the frame structure. The current LTE subframe length is 1 ms. Because adaptive retransmission is supported, one time and one time, each time delay is at least 8 ms, and several times, the delay of the optical interface is ten ms. In order to reduce the delay, the length of the physical frame needs to be further shortened. If adaptive retransmission is adopted, the round trip time should be much less than 5 ms each time.
In high-reliability transmission applications, the LTE for general data in the air interface error rate (FER) requirement is 10% of the initial transmission. After several retransmissions (of course, the delay is increased), if the block error rate is less than 1%, can. Obviously this is far from meeting the 99.999% reliability requirement. In order to further improve the system performance, we can first consider using the new channel coding technology to reduce the block error rate to one in 100,000 without significantly increasing the delay. Or use a more efficient forward error correction coding (FEC) low-latency and high-reliability transmission mechanism: by sacrificing the rate (or bandwidth), the probability of information retransmission can be greatly reduced, thereby effectively reducing the transmission delay.
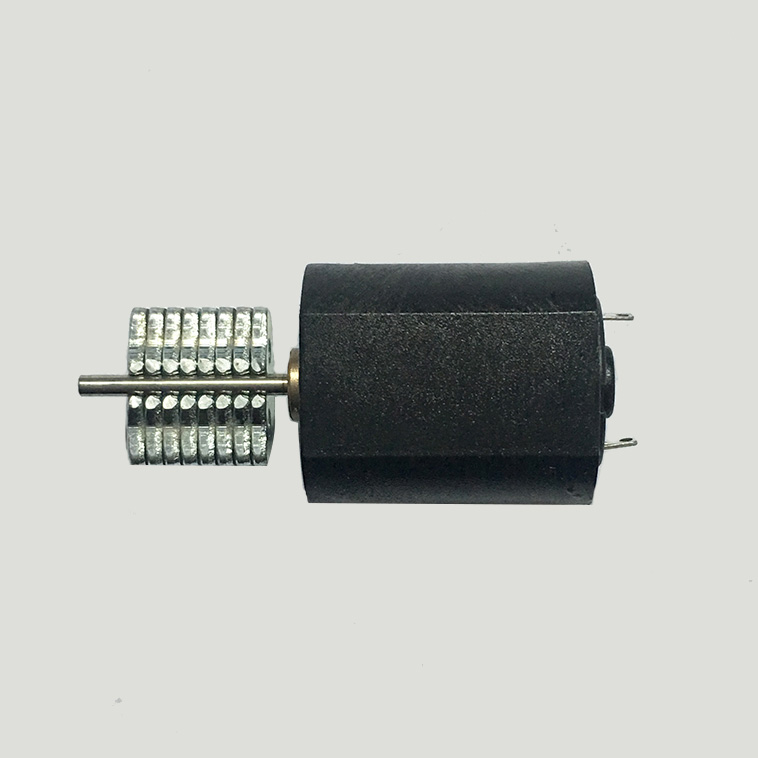
The Micro Vibration Motor is introduced:
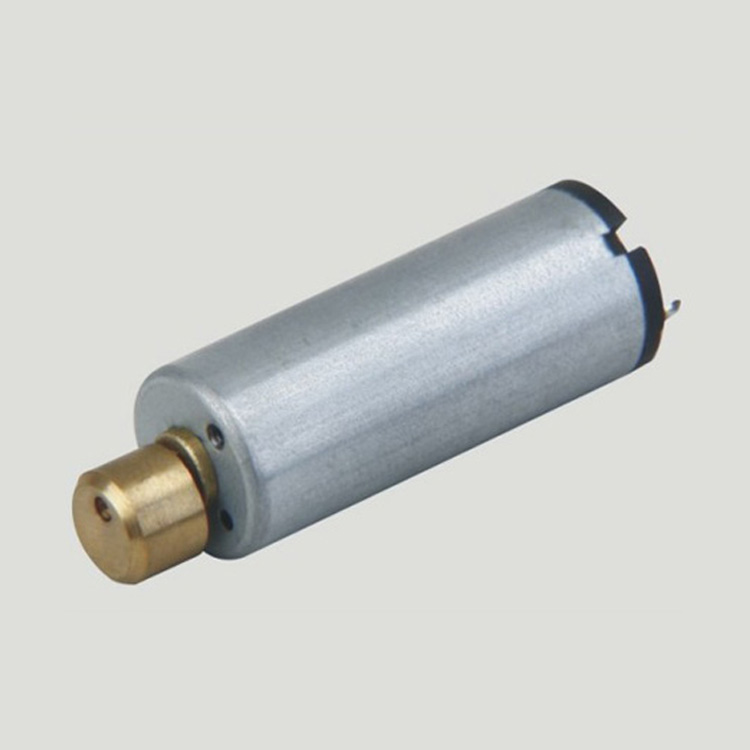
Micro Vibration Motor is mainly used for adult health care products and toys, micro vibration motor is a Dc Motor, the motor shaft with an eccentric wheel, the use of most of the micro vibration motor voltage is lower than 6 v, probably between 6 mm to 15 mm in diameter, when the motor rotation, eccentric circle particles is not the core of the motor, the motor often lose their balance, due to the inertia effect.
Characteristics: small volume, strong vibration;
Features: small size, fast speed, stable performance, low price, can use battery drive,Can change the different materials of the pendulum head

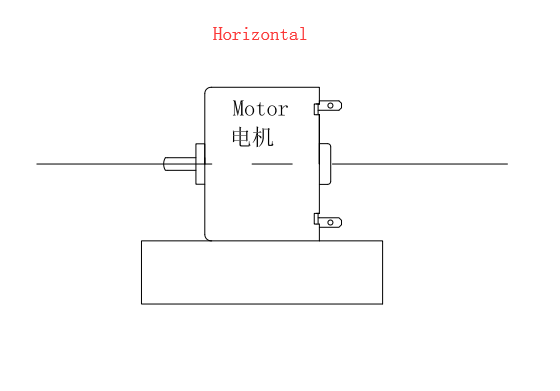
Method of use: the best stable in horizontal plane, installed on the dc Micro vibration motor output shaft parts, cannot use a hammer to knock, knock prone to press into the Micro vibration motor drive, may cause damage to internal components, and cannot be used in the case of blocked.
Operating temperature range:
Mini Vibration Motor should be used at a temperature of -10~60℃.
The figures stated in the catalog specifications are based on use at ordinary room temperature catalog specifications re based on use at ordinary room temperature (approximately20~25℃.
If a Mini Vibration Motor is used outside the prescribed temperature range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.Depending on the temperature conditions ,it may be possible to deal with them by changing the grease of the motor's parts.Please feel free to consult with us about this.
Storage temperature range:
Mini Vibration Motor should be stored ta a temperature of -15~65℃.
In case of storage outside this range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.
Service life:
The longevity of Mini Vibration Motor is greatly affected by the load conditions , the mode of operation,the environment of use ,etc.Therefore,it is necessary to check the conditions under which the product will actually be used .The following conditions will have a negative effect on longevity.Please consult with us should any of them apply.
â—Use with a load that exceeds the rated torque
â—Frequent starting
â—Momentary reversals of turning direction
â—Impact loads
â—Long-term continuous operation
â—Forced turning using the output shaft
â—Use in which the permitted overhang load or the permitted thrust load is exceeded
â—A pulse drive ,e.g.,a short break,counter electromotive force,PWM control
â—Use of a voltage that is nonstandard as regards the rated voltage
â—Use outside the prescribed temperature or relative-humidity range,or in a special environment.
â—Please consult with us about these or any other conditions of use that may apply,so that we can be sure that you select the most appropriate model.
when it come to volume production,we're a major player as well .each month,we rurn out 600000 units,all of which are compliant with the rohs directive.Have any questions or special needed, please contact us, we have the engineer group and best sales department to service to you Looking forward to your inquiry. Welcome to our factory.

Micro Vibration Motor
Micro Vibration Motor,Mini Vibration Motor,Dc Micro Vibration Motor,Electric Micro Vibration Motor
Shenzhen Shunchang Motor Co., LTD. , https://www.scgearmotor.com